Configuring OpenID Connect for Google Kubernetes Engine
This document outlines the steps required to configure Pulumi to accept Google Kubernetes Engine id_tokens to be exchanged for Organization access tokens. With this configuration, Kubernetes pods authenticate to Pulumi Cloud using OIDC tokens issued by GKE.
See “Bound Tokens” for more background.
Prerequisites
- You must be an admin of your Pulumi organization.
- You must have a GKE cluster.
Please note that this guide provides step-by-step instructions based on the official provider documentation which is subject to change. For the most current and precise information, always refer to the official Bound Service Account Tokens documentation.
Register the OIDC issuer
- Navigate to OIDC Issuers under your Organization’s Settings and click on Register a new issuer.
- Name the issuer and complete the url:
https://container.googleapis.com/v1/projects/PROJECT_NAME/locations/LOCATION/clusters/CLUSTER_NAME/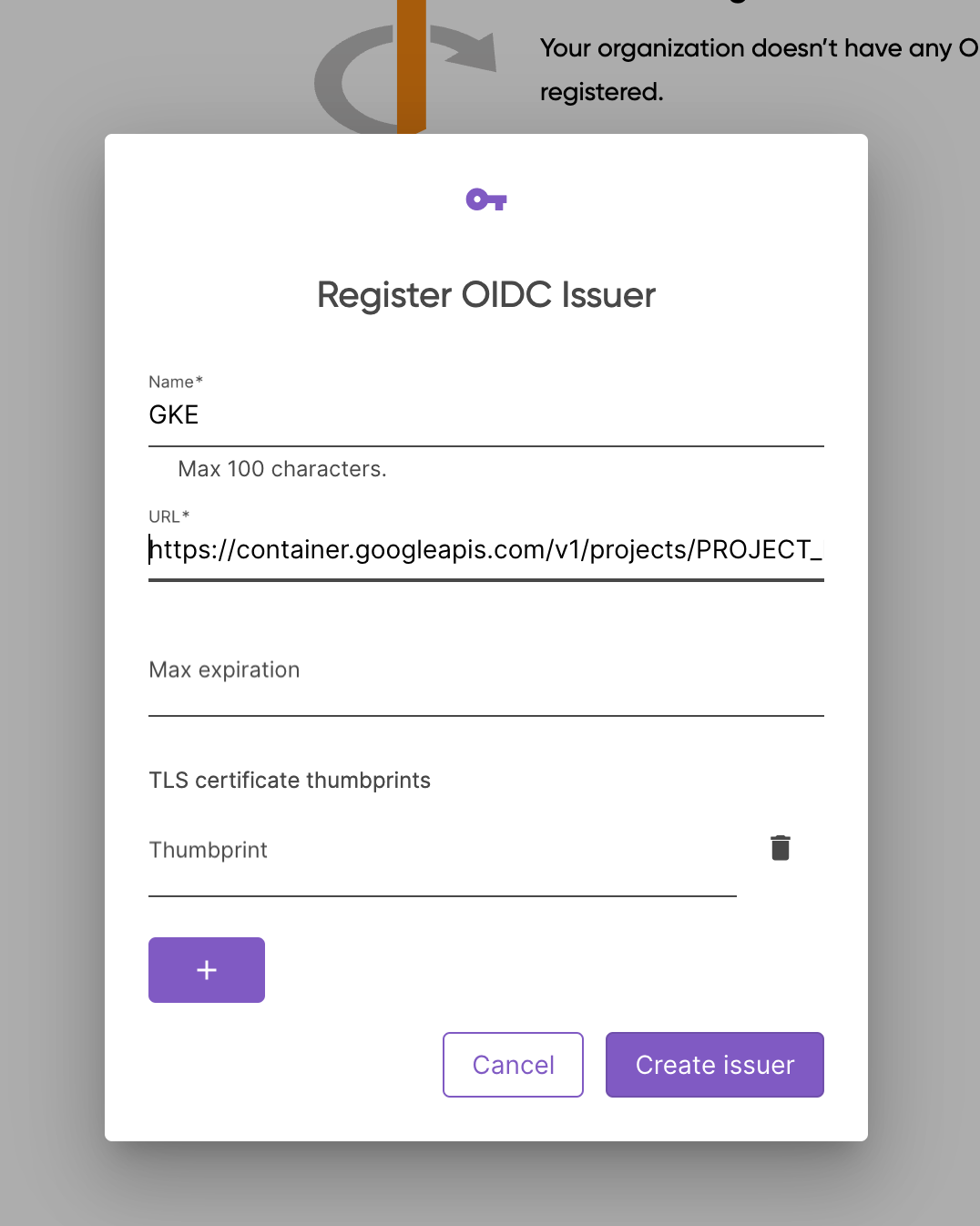
- Submit the form
Configure the Authorization Policies
- Click on the issuer name
- Change the policy decision to
Allow - Change the token type to
Organization - Add a new rule and configure it to verify namespace and the service name:
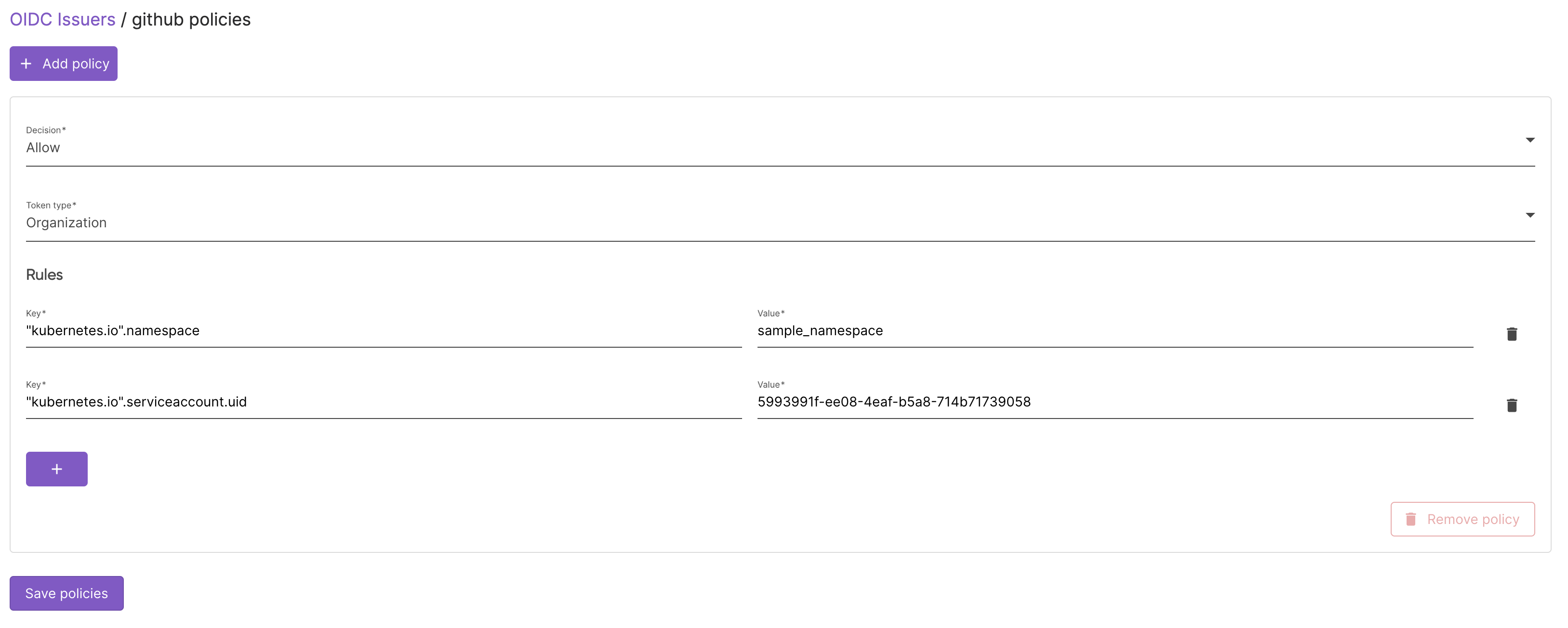
- Click on update
Sample
// Pulumi program to run a bash script in a Kubernetes pod,
// mount a service account token with an appropriate audience,
// exchange the token for an ordinary Pulumi access token,
// then run `pulumi whoami`.
import * as kubernetes from "@pulumi/kubernetes";
const tokenParams = {
"audience": "urn:pulumi:org:ORG_NAME",
"token_type": "urn:pulumi:token-type:access_token:organization",
"expiration": 2 * 60 * 60,
}
const script = new kubernetes.core.v1.ConfigMap("script", {
data: {
"entrypoint.sh": `#!/bin/bash
apt -qq install -y jq
OIDC_GKE_TOKEN=$(</var/run/secrets/pulumi/token)
echo "OIDC Token:"
echo $OIDC_GKE_TOKEN
export PULUMI_ACCESS_TOKEN=$(curl -sS -X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \
-d 'audience=${tokenParams.audience}' \
-d 'grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:token-exchange' \
-d 'subject_token_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:token-type:id_token' \
-d 'requested_token_type=${tokenParams.token_type}' \
-d 'expiration=${tokenParams.expiration}' \
-d 'scope=${tokenParams.scope}' \
-d "subject_token=$OIDC_GKE_TOKEN" \
https://api.pulumi.com/api/oauth/token | jq -r '.access_token')
echo "Access Token:"
echo $PULUMI_ACCESS_TOKEN
pulumi whoami
`
}
});
const job = new kubernetes.batch.v1.Job("runner", {
metadata: {
},
spec: {
template: {
spec: {
containers: [{
name: "runner",
image: "pulumi/pulumi:latest",
command: ["/bin/entrypoint.sh"],
volumeMounts: [
{
name: "pulumi-serviceaccounttoken",
mountPath: "/var/run/secrets/pulumi",
},
{
name: "script",
mountPath: "/bin/entrypoint.sh",
readOnly: true,
subPath: "entrypoint.sh",
},
],
}],
restartPolicy: "Never",
volumes: [
{
name: "pulumi-serviceaccounttoken",
projected: {
sources: [
{
serviceAccountToken: {
audience: "urn:pulumi:org:ORG_NAME",
expirationSeconds: 3600,
path: "token",
},
},
],
},
},
{
name: "script",
configMap: {
defaultMode: 0o700,
name: script.metadata.name,
},
},
],
},
},
backoffLimit: 0,
},
});
export const jobName = job.metadata.name;
Thank you for your feedback!
If you have a question about how to use Pulumi, reach out in Community Slack.
Open an issue on GitHub to report a problem or suggest an improvement.