Using Pulumi Deployments
This page highlights some common patterns and workflows using Pulumi Deployments.
Deployment Settings
Deployment settings refer to the full set of configuration required to run a Pulumi Deployment, defined on a per-stack basis. These settings may be defined once for the stack, via the UI, Pulumi Service provider, or the REST API and can be consumed using any of the triggers, i.e., push-to-deploy, click-to-deploy, or via the REST API.
From the Pulumi Cloud UI
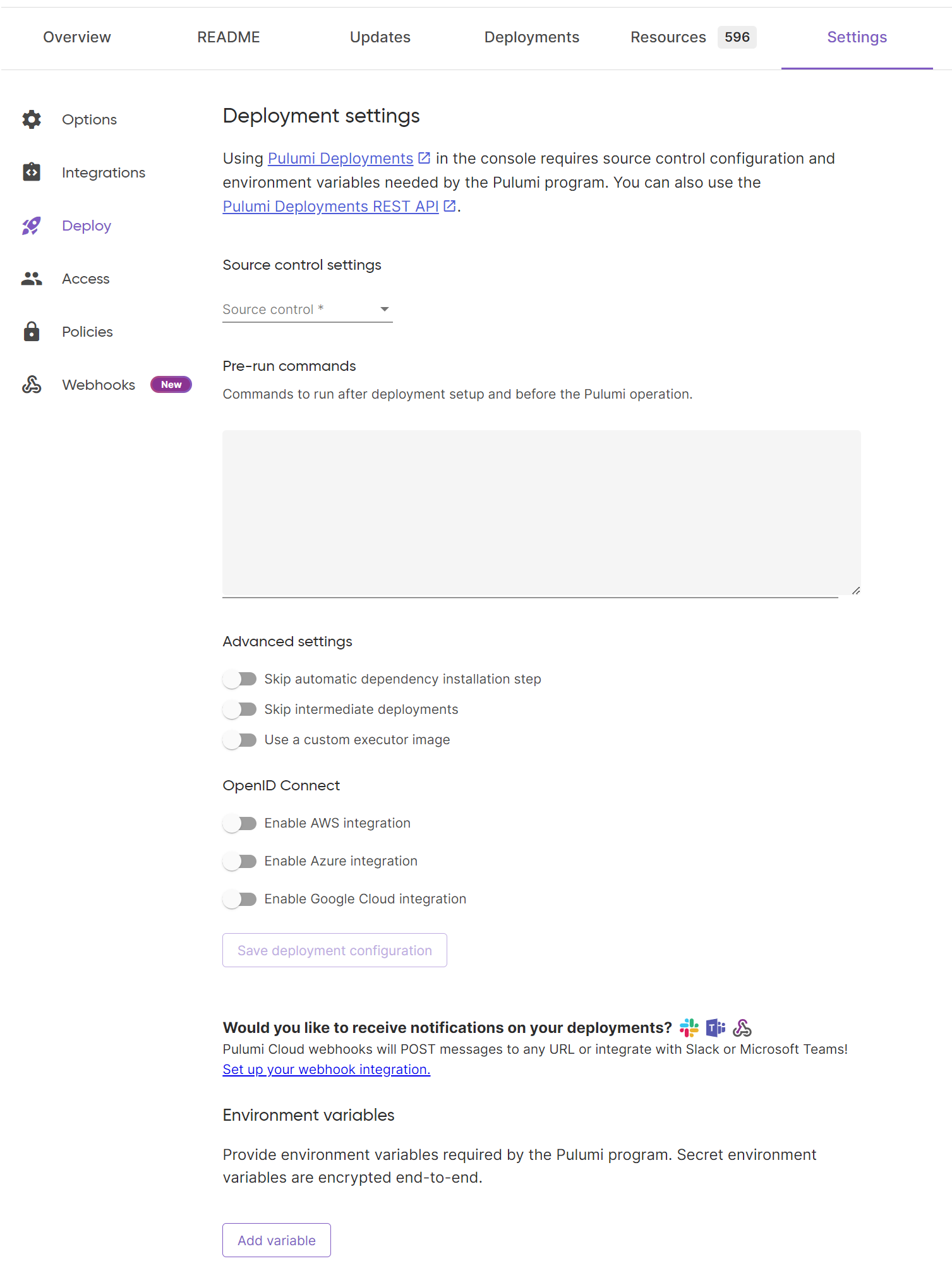
From the Pulumi Console, a stack’s deployment settings can be accessed via the Settings > Deploy tab. Once the settings are defined via the UI, they apply to all Deployment triggers, including push-to-deploy (if you have the GitHub app installed), click-to-deploy and the REST API.
From the API
Alternatively, a stack’s deployment settings may be defined and subsequently modified using the REST API.
POST https://api.pulumi.com/{org}/{project}/{stack}/deployment/settings
{
"sourceContext": {
"git": {
"repoURL": "https://github.com/pulumi/deploy-demos.git",
"branch": "main",
"repoDir": "pulumi-programs/simple-resource"
}
},
"operationContext": {
"environmentVariables": {
"TEST_VAR": "foo",
"SECRET_VAR": {
"secret": "my-secret"
}
}
}
}
To modify an environment variable in the deployment settings, you only need to specify the changed settings:
POST https://api.pulumi.com/api/stacks/{org}/{project}/{stack}/deployments/settings
{
"operationContext": {
"environmentVariables": {
"TEST_VAR": "new_value"
}
}
}
The REST API documentation contains much more thorough information about individual API properties.
Defined as Code with the Pulumi Cloud Service provider
Finally, a stack’s deployment settings may be defined as a resource within the stack itself using the Pulumi Service provider. This lets you securely store your settings in source control alongside your code.
We recommend that a stack does not configure it’s own Deployment Settings, as this would require two deployments for settings changes to take effect. Typically, users create a stack per cloud environment that defines Deployment Settings for all other stacks that deploy into that account or environment. This enables centralizing and sharing common configuration such as OIDC providers. Commonly, these stacks that manage Deployment Settings are themselves managed by Pulumi Deployments and benefit from the pull request and code review workflow.
import * as pulumi from "@pulumi/pulumi";
import * as service from "@pulumi/pulumiservice";
const config = new pulumi.Config();
const settings = new service.DeploymentSettings("deployment_settings", {
organization: "service-provider-test-org",
project: "test-deployment-settings-project",
stack: "dev",
operationContext: {
environmentVariables: {
TEST_VAR: "foo",
SECRET_VAR: config.requireSecret("my_secret"),
}
},
sourceContext: {
git: {
repoUrl: "https://github.com/pulumi/deploy-demos.git",
branch: "refs/heads/main",
repoDir: "pulumi-programs/simple-resource"
}
}
});
Deployment Triggers
A deployment trigger refers to a method of initializing a deployment. Currently, a deployment may be triggered using the REST API, by clicking a button in the Pulumi Console, via a Review Stack, or via a git push if the GitHub application is installed.
REST API
Once deployment settings are defined for a stack, triggering a deployment is as simple as a one-line request.
POST https://api.pulumi.com/api/stacks/{org}/{project}/{stack}/deployments
{
"operation": "update/preview/refresh/destroy"
}
If you need to override some specific settings, you can specify them in the request body.
POST https://api.pulumi.com/api/stacks/{org}/{project}/{stack}/deployments
{
"operation": "update/preview/refresh/destroy",
"operationContext": {
"environmentVariables": {
"EXTRA_VAR": {
"secret": "my-super-secret-value"
}
}
}
}
If you would rather not use the predefined settings at all, you must set inheritSettings to false in your request body and define the entire settings object.
The merge behavior of deployment settings are further explained in the REST API documentation.
Click to Deploy
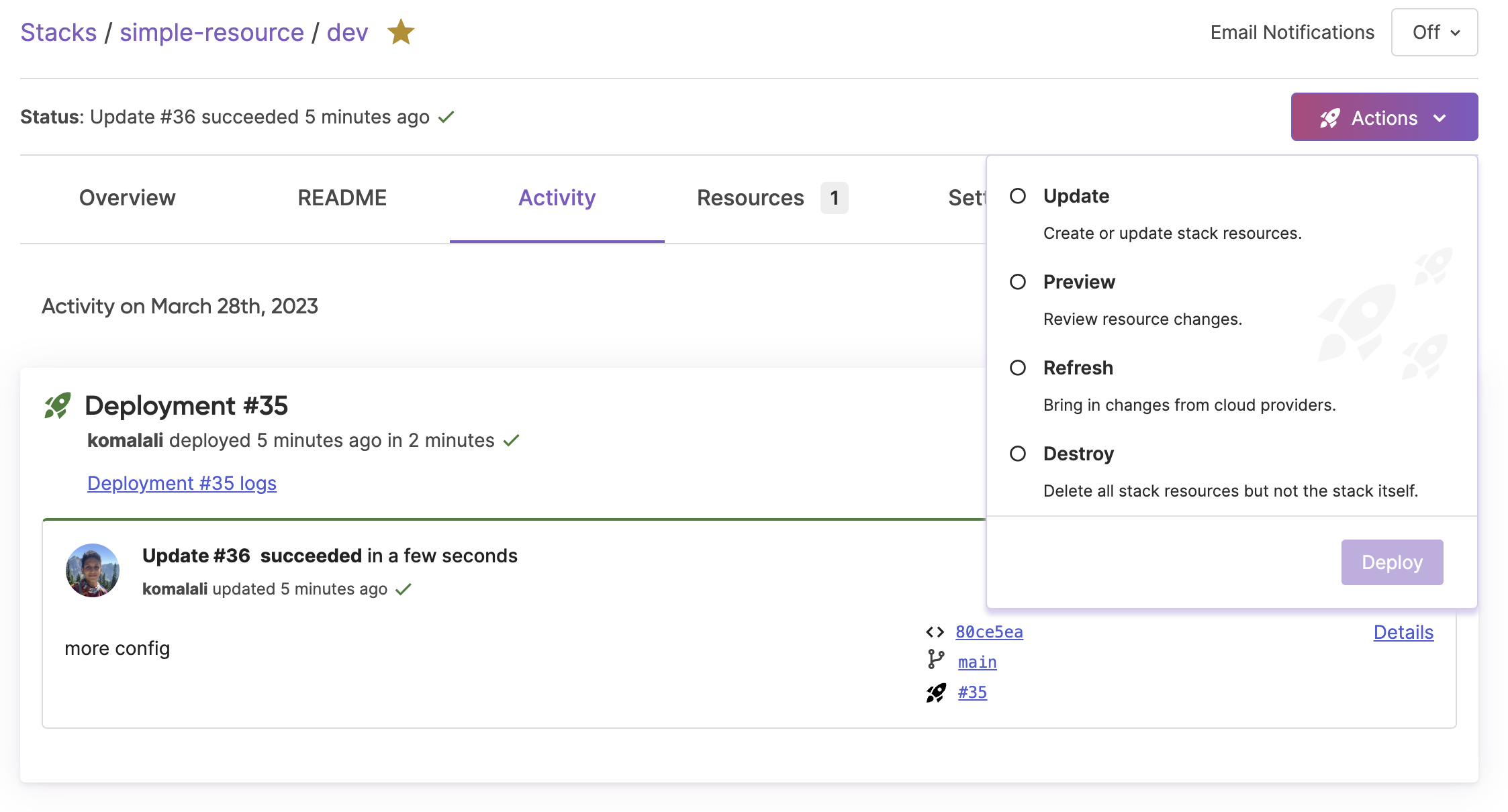
A deployment may be triggered at the simple click of a button in the Pulumi Console. Useful to test if your deployment settings are configured correctly or to execute one-off deployments.
GitHub Push to Deploy
Once you have the GitHub application installed in your Pulumi organization, you can choose to have deployments run a pulumi preview when Pull Requests are opened against a target branch, or pulumi up when a commit is pushed to a branch.
pulumi preview on Pull Request capability requires that the Github user creating the Pull Request has their Github Organization Visibility set to Public.
Review Stacks
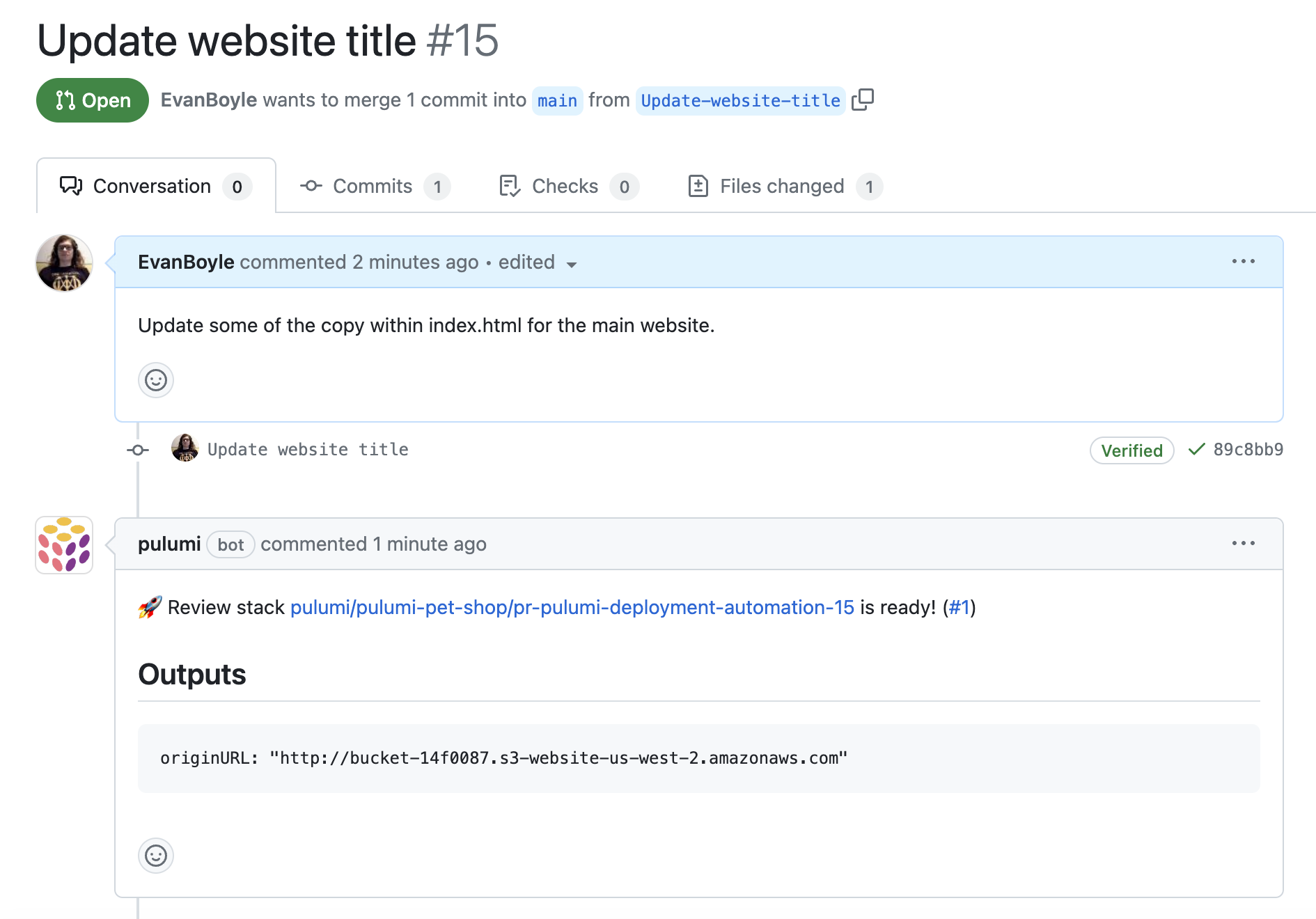
Review Stacks are dedicated cloud environments that get created automatically every time a pull request is opened, all powered by Pulumi Deployments. Open a pull request, and Pulumi Deployments will stand up a stack with your changes and the Pulumi GitHub App will add a PR comment with the outputs from your deployment. Merge the PR and Pulumi Deployments will destroy the stack and free up the associated resources.
Configuring push-to-deploy from GitHub
GitHub App Installation
You’ll need to install and configure the Pulumi GitHub App to use push-to-deploy functionality. The app requires read access to your repos so it can clone your Pulumi programs and listen to merge commits to automatically trigger deployments on git push.
Follow these steps:
Ensure you have selected the Pulumi organization you wish to use with Pulumi Deployments in the Organization drop-down.
Navigate to Settings > Integrations.
Select the “Install the Pulumi GitHub App” button.
If this page says you already have the app installed, you can stop here. If the page asks you to accept additional permissions for the app, please accept the permissions and stop here.
After clicking “Install” you will be directed to GitHub. Select the GitHub organization you wish to use with Pulumi Deployments.
Select which repos (or all repos) Pulumi Deployments can have access to, and then Install.
You will be redirected to the Pulumi Cloud (app.pulumi.com). Return to Settings > Integrations to confirm the GitHub App is installed.
If you installed the GitHub app in the past and the steps above aren’t showing it as installed for your desired organization, please try the following:
- Ensure you’re a GitHub admin of the GitHub organization where you’re installing the app.
- Uninstall the app (via GitHub) and re-install it following the steps above. Note: Uninstalling the app will delete any push-to-deploy configurations you may have already setup.
Configuring settings
Once the GitHub app has been installed, the deployment settings for a stack can be defined using the methods defined in the Deployment Settings section.
Limitations
- The GitHub app may only be installed by a GitHub and Pulumi admin.
- Currently, there is a 1 to 1 mapping between GitHub organizations and Pulumi organizations.
Common Scenarios
Environment variables
By default, there are a set of environment variables set by the process automatically:
GITHUB_TOKEN: Personal Access Token configured when the source is GitHub (unless there is a token configured by the custom environment variables)PULUMI_ACCESS_TOKEN: A temporary token with read-write access only to the stack being deployed.PULUMI_DEPLOY_OIDC_CONFIG: OIDC configuration provided for the cloud integrationsPULUMI_CI_SYSTEM: “Pulumi Deployments”PULUMI_CI_BUILD_ID: Current deployment IDPULUMI_CI_BUILD_NUMBER: Current deployment versionPULUMI_CI_BUILD_URL: Current deployment URLPULUMI_CI_ORGANIZATION: Current account organizationPULUMI_CI_PROJECT: Current project namePULUMI_CI_STACK: Current stack name
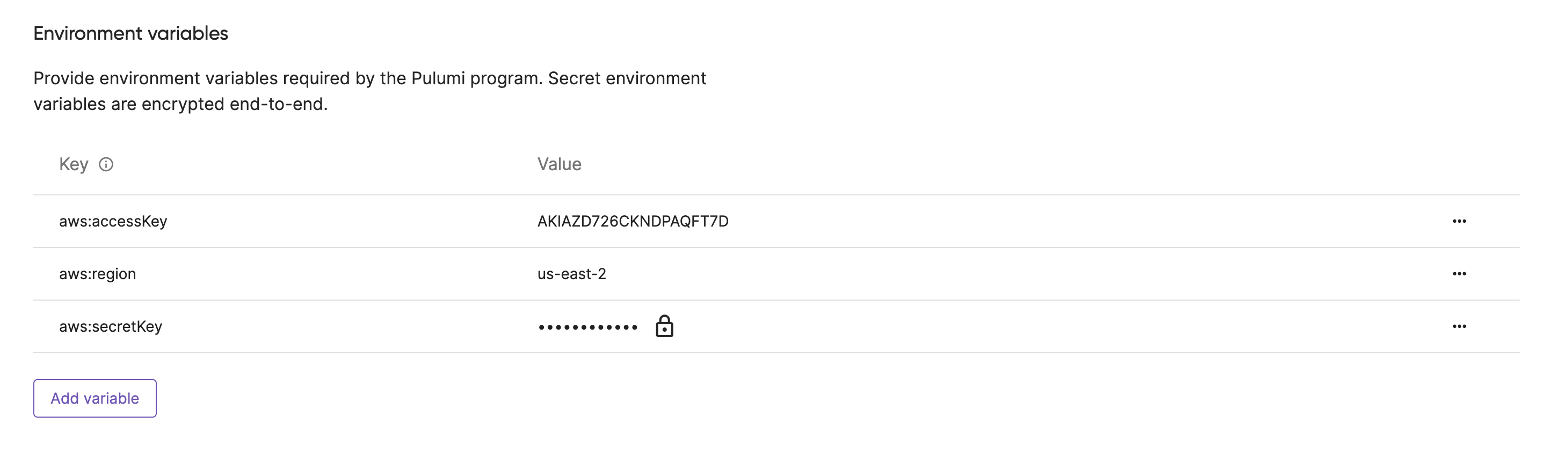
These can be overridden or extended by configuring custom environment variables:
PULUMI_ENV
Environment variables can be persisted between pre-run commands and the final pulumi deployment by appending them to the file on the file system named PULUMI_ENV.
Example Usage:
export GOOGLE_OAUTH_ACCESS_TOKEN=$(gcloud auth print-access-token)
echo GOOGLE_OAUTH_ACCESS_TOKEN=$GOOGLE_OAUTH_ACCESS_TOKEN >> /PULUMI_ENV
Running env in a subsequent pre-run command will show the environment variable and it should be usable by scripts or your pulumi program.
/PULUMI_ENV does not work, and you are on self hosted, you can look for the following message in the logs to get the location: Loading PULUMI_ENV from.Deployment permissions
By default, the permissions that are granted to a deployment depend on how the deployment is being invoked. If the
deployment is created via the REST API or by using the Actions buttons in the Pulumi Cloud console, it is
granted the permissions of the user that has executed the action. However, if a deployment is created because of a git push
or a pull request, it uses an ephemeral stack token that has admin permissions on only the stack itself, but nothing
else.
In practice, the consequences of this are twofold:
- If your organization has default stack permissions set to
NONE, then any deployment created by agit pushor a pull request will not be able to access any Stack References, and will fail if it tries to do so. - If your organization has default environment permissions set to
NONE, then any deployment created by agit pushor a pull request will not be able to access any ESC Environments that are listed in the stack’s configuration file.
Granting extra permissions to a deployment
If you want to change the permissions that are granted to a deployment, you can do so by setting the PULUMI_ACCESS_TOKEN
environment variable to a token with the desired permissions in the stack’s deployment settings. This token can be an individual,
team or organization token, and it will grant the deployment the permissions that are associated with the token. If this
environment variable is set it will be used regardless of how the deployment was created (REST API, git push, etc.).
If using an individual or team token, the token must have at minimum:
WRITEaccess to the stack that is being deployedREADaccess to any stacks from which Stack References are being usedOPENaccess to any ESC environment that is listed in the stack’s configuration file, including any environments that are imported transitively.
Path filtering
When using the GitHub app and push-to-deploy, you may want to filter deployment events to only target file changes in specific directories. You can easily do this using path filtering, so a deployment is only triggered if there is a change in files that match the path filters. This is especially useful for monorepos where you may have multiple Pulumi programs within the same repository.
Path filters are relative to the repository root, and should reference a file by name or a directory must reference files by name relative to the repository or directories via glob patterns such as /** to include all changes within a directory.
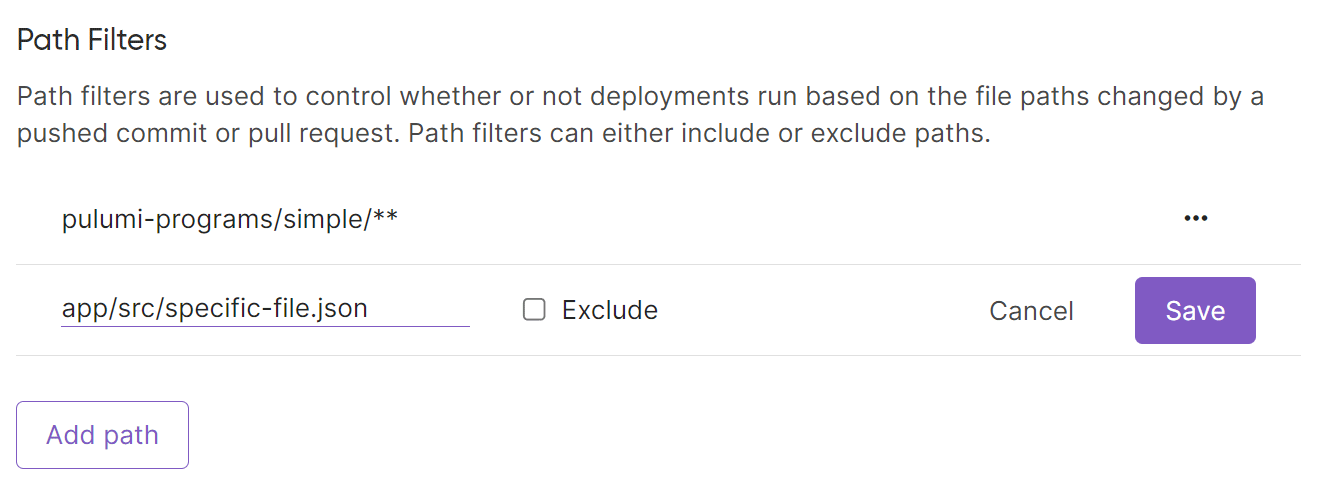
As with any other deployment setting, the path filters may be set via the Pulumi Console, using the REST API or defined in code using the Service provider.
Private dependency packages
If your Pulumi Deployment requires access to private GitHub repositories, e.g. your program uses a private Go module, it is necessary to configure an SSH key with access to the required repos. Without the correct configuration, the Deployment will be unable to access those private artifacts, and the deployment may fail.
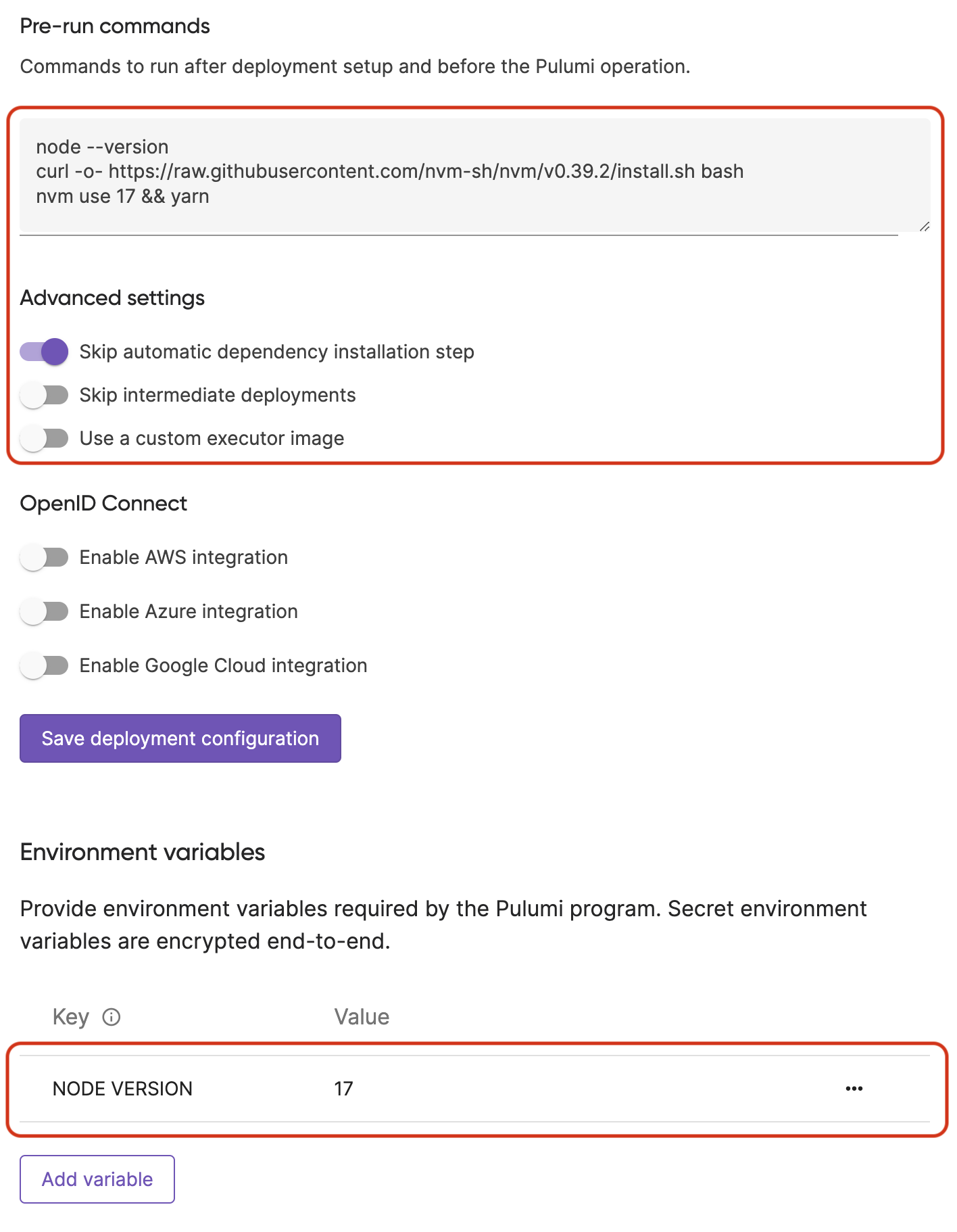
The following will allow you to configure a private key and allow access to GitHub using SSH to pull down the appropriate artifacts properly:
Add the following code into the
Pre-run commandsand toggle onSkip automatic dependency installation stepin Advanced Settings:mkdir /root/.ssh && printf -- "$SSHKEY" > /root/.ssh/id_ed25519 chmod 600 /root/.ssh/id_ed25519 ssh-keyscan github.com >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts cd .. && git config --global --add url.\"git@github.com:\".insteadOf \"https://github.com\"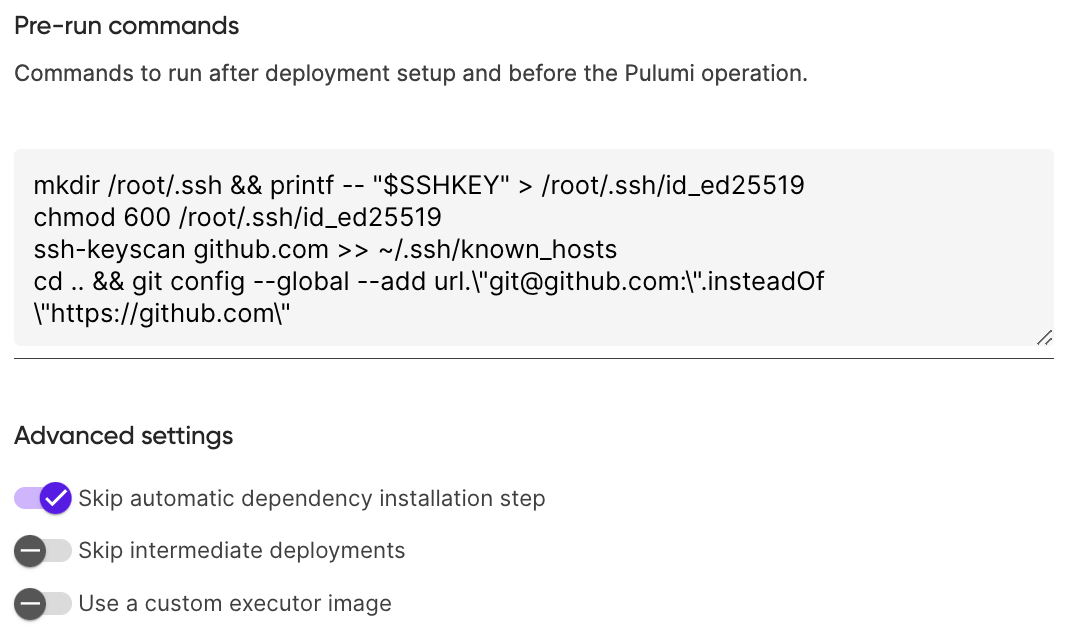
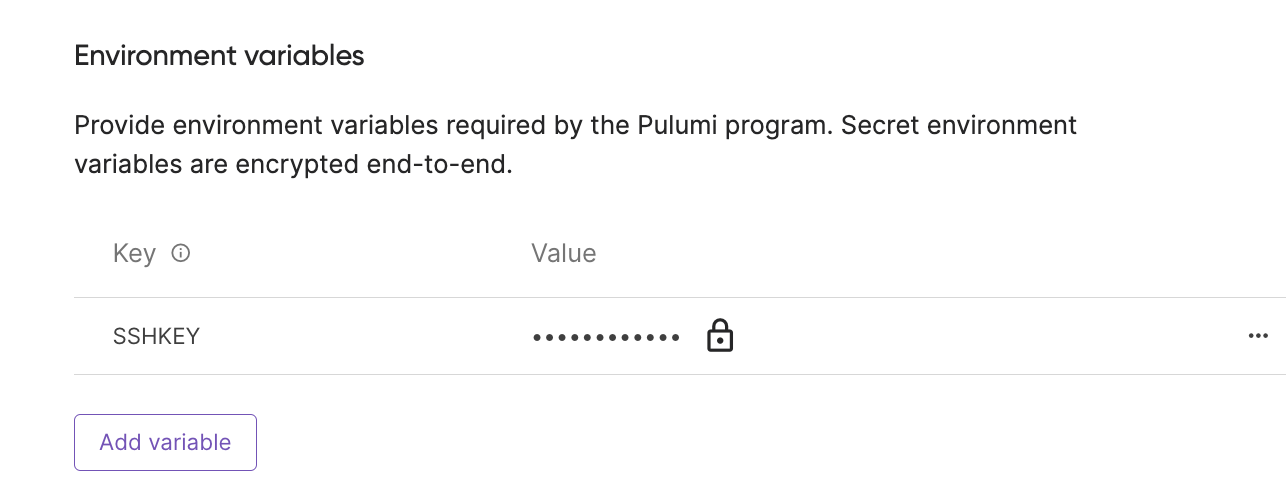
Add the
$SSHKEYfield as a secret environment variable:
Skip intermediate deployments
By default, when multiple deployments are pushed, they will be executed sequentially until the backlog is completed. In some cases, you may wish to only execute the most recent deployment since the changes are accumulative. By enabling the Skip intermediate deployments setting, Pulumi will skip all intermediary deployments of the same type and will execute only the latest.

Customizing the deployment environment
By default, the deployment is executed using the pulumi/pulumi image.
The pulumi/pulumi image is a unix-based image which includes the pulumi CLI in its $PATH and the LTS versions of all supported SDK runtime(s) for your Pulumi program.
However, there may be scenarios where you might want to customize the image used for the execution, e.g. if you want to use a different version of python or need to include additional dependencies.
This is possible by specifying a custom executor image for your deployment. Using the custom executor image field, you can pin to a specific version of the pulumi/pulumi image, or point to a completely custom image hosted in a public or private container registry.
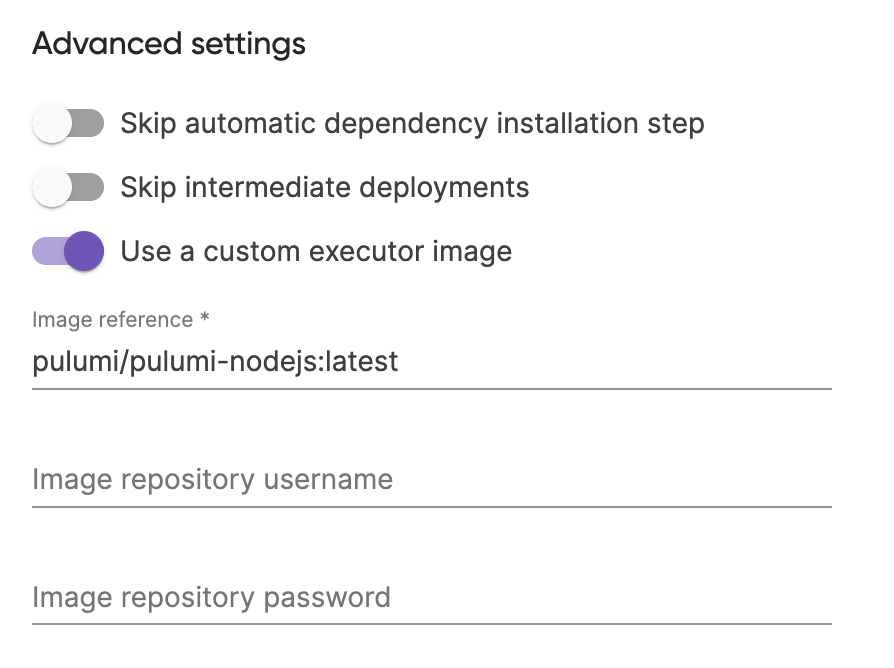
Image requirements:
- It must be a unix-based image which includes
curl. - It must include the
pulumiCLI in its$PATH. - It must include the required SDK runtime(s) for your Pulumi program.
Customizing the dependency installation step
By default, the deployment executor will attempt to install dependencies for your project by using the default dependency manager for the language (i.e. npm for nodejs or virtualenv for python). However, there may be scenarios where you may want to have more control over the dependency installation step (e.g. you are using yarn and/or a different version of node than the one that is installed by default).
This is enabled by skipping the default dependency installation step (under Advanced Settings in the UI), and setting a few pre-run commands and environment variables.
Deploying dependent stacks
Pulumi Deployments can be used to automatically deploy dependent stacks via Deployment Webhooks. This enables you to keep your infrastructure up-to-date across stack reference boundaries. This can be configured in one of two ways:
Either method requires that your stacks are configured with Deployment Settings.
Deployment webhook destinations
Deployment Webhook Destinations allow you to pick one or more event types on a stack (i.e. update succeeded, or refresh failed) and automatically deliver an event to a destination - in this case the Create Deployment API for another Stack.
import * as pulumi from "@pulumi/pulumi";
import * as pulumiservice from "@pulumi/pulumiservice";
const databaseWebhook = new pulumiservice.Webhook("databaseWebhook", {
organizationName: "org",
projectName: "network",
stackName: "prod",
format: pulumiservice.WebhookFormat.PulumiDeployments,
payloadUrl: "database/prod",
active: true,
displayName: "deploy-database",
filters: [pulumiservice.WebhookFilters.UpdateSucceeded],
});
const computeWebhook = new pulumiservice.Webhook("computeWebhook", {
organizationName: "org",
projectName: "database",
stackName: "prod",
format: pulumiservice.WebhookFormat.PulumiDeployments,
payloadUrl: "compute/prod",
active: true,
displayName: "deploy-compute",
filters: [pulumiservice.WebhookFilters.UpdateSucceeded],
});
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using Pulumi;
using PulumiService = Pulumi.PulumiService;
return await Deployment.RunAsync(() =>
{
var databaseWebhook = new PulumiService.Webhook("databaseWebhook", new()
{
OrganizationName = "org",
ProjectName = "network",
StackName = "prod",
Format = PulumiService.WebhookFormat.PulumiDeployments,
PayloadUrl = "database/prod",
Active = true,
DisplayName = "deploy-database",
Filters = new[]
{
PulumiService.WebhookFilters.UpdateSucceeded,
},
});
var computeWebhook = new PulumiService.Webhook("computeWebhook", new()
{
OrganizationName = "org",
ProjectName = "database",
StackName = "prod",
Format = PulumiService.WebhookFormat.PulumiDeployments,
PayloadUrl = "compute/prod",
Active = true,
DisplayName = "deploy-compute",
Filters = new[]
{
PulumiService.WebhookFilters.UpdateSucceeded,
},
});
});
import pulumi
import pulumi_pulumiservice as pulumiservice
database_webhook = pulumiservice.Webhook("databaseWebhook",
organization_name="org",
project_name="network",
stack_name="prod",
format=pulumiservice.WebhookFormat.PULUMI_DEPLOYMENTS,
payload_url="database/prod",
active=True,
display_name="deploy-database",
filters=[pulumiservice.WebhookFilters.UPDATE_SUCCEEDED])
compute_webhook = pulumiservice.Webhook("computeWebhook",
organization_name="org",
project_name="database",
stack_name="prod",
format=pulumiservice.WebhookFormat.PULUMI_DEPLOYMENTS,
payload_url="compute/prod",
active=True,
display_name="deploy-compute",
filters=[pulumiservice.WebhookFilters.UPDATE_SUCCEEDED])
package main
import (
"github.com/pulumi/pulumi-pulumiservice/sdk/go/pulumiservice"
"github.com/pulumi/pulumi/sdk/v3/go/pulumi"
)
func main() {
pulumi.Run(func(ctx *pulumi.Context) error {
_, err := pulumiservice.NewWebhook(ctx, "databaseWebhook", &pulumiservice.WebhookArgs{
OrganizationName: pulumi.String("org"),
ProjectName: pulumi.String("network"),
StackName: pulumi.String("prod"),
Format: pulumiservice.WebhookFormatPulumiDeployments,
PayloadUrl: pulumi.String("database/prod"),
Active: pulumi.Bool(true),
DisplayName: pulumi.String("deploy-database"),
Filters: pulumiservice.WebhookFiltersArray{
pulumiservice.WebhookFiltersUpdateSucceeded,
},
})
if err != nil {
return err
}
_, err = pulumiservice.NewWebhook(ctx, "computeWebhook", &pulumiservice.WebhookArgs{
OrganizationName: pulumi.String("org"),
ProjectName: pulumi.String("database"),
StackName: pulumi.String("prod"),
Format: pulumiservice.WebhookFormatPulumiDeployments,
PayloadUrl: pulumi.String("compute/prod"),
Active: pulumi.Bool(true),
DisplayName: pulumi.String("deploy-compute"),
Filters: pulumiservice.WebhookFiltersArray{
pulumiservice.WebhookFiltersUpdateSucceeded,
},
})
if err != nil {
return err
}
return nil
})
}
name: auto-deploy-demo
runtime: yaml
description: A simple auto-deploy example
resources:
databaseWebhook:
type: pulumiservice:Webhook
properties:
organizationName: org
projectName: network
stackName: prod
format: pulumi_deployments
payloadUrl: database/prod
active: true
displayName: deploy-database
filters:
- update_succeeded
computeWebhook:
type: pulumiservice:Webhook
properties:
organizationName: org
projectName: database
stackName: prod
format: pulumi_deployments
payloadUrl: compute/prod
active: true
displayName: deploy-compute
filters:
- update_succeeded
Pulumi Auto Deploy
Pulumi Auto Deploy lets you simply express dependencies between stacks, and takes care of creating and updating the necessary Deployment Webhooks under the hood.
import * as autodeploy from "@pulumi/auto-deploy";
import * as pulumi from "@pulumi/pulumi";
/**
*
* The following example configures automatic deployment of stacks with the following dependency graph:
a
├── b
│ ├── d
│ ├── e
│ └── f
└── c
* Whenever a node in the graph is updated,
* all downstream nodes will be automatically updated via a webhook triggering Pulumi Deployments.
*/
const organization = pulumi.getOrganization();
const project = "dependency-example"
export const f = new autodeploy.AutoDeployer("auto-deployer-f", {
organization,
project,
stack: "f",
downstreamRefs: [],
});
export const e = new autodeploy.AutoDeployer("auto-deployer-e", {
organization,
project,
stack: "e",
downstreamRefs: [],
});
export const d = new autodeploy.AutoDeployer("auto-deployer-d", {
organization,
project,
stack: "d",
downstreamRefs: [],
});
export const c = new autodeploy.AutoDeployer("auto-deployer-c", {
organization,
project,
stack: "c",
downstreamRefs: [],
});
export const b = new autodeploy.AutoDeployer("auto-deployer-b", {
organization,
project,
stack: "b",
downstreamRefs: [d.ref, e.ref, f.ref],
});
export const a = new autodeploy.AutoDeployer("auto-deployer-a", {
organization,
project,
stack: "a",
downstreamRefs: [b.ref, c.ref],
});
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using Pulumi;
using AutoDeploy = Pulumi.AutoDeploy;
/**
*
* The following example configures automatic deployment of stacks with the following dependency graph:
a
├── b
│ ├── d
│ ├── e
│ └── f
└── c
* Whenever a node in the graph is updated,
* all downstream nodes will be automatically updated via a webhook triggering Pulumi Deployments.
*/
return await Deployment.RunAsync(() =>
{
var projectVar = "dependency-example";
var organization = "pulumi";
var f = new AutoDeploy.AutoDeployer("f", new()
{
Organization = organization,
Project = projectVar,
Stack = "f",
DownstreamRefs = new[] {},
});
var e = new AutoDeploy.AutoDeployer("e", new()
{
Organization = organization,
Project = projectVar,
Stack = "e",
DownstreamRefs = new[] {},
});
var d = new AutoDeploy.AutoDeployer("d", new()
{
Organization = organization,
Project = projectVar,
Stack = "d",
DownstreamRefs = new[] {},
});
var c = new AutoDeploy.AutoDeployer("c", new()
{
Organization = organization,
Project = projectVar,
Stack = "c",
DownstreamRefs = new[] {},
});
var b = new AutoDeploy.AutoDeployer("b", new()
{
Organization = organization,
Project = projectVar,
Stack = "b",
DownstreamRefs = new[]
{
d.Ref,
e.Ref,
f.Ref,
},
});
var a = new AutoDeploy.AutoDeployer("a", new()
{
Organization = organization,
Project = projectVar,
Stack = "a",
DownstreamRefs = new[]
{
b.Ref,
c.Ref,
},
});
});
import pulumi
import pulumi_auto_deploy as auto_deploy
'''
The following example configures automatic deployment of stacks with the following dependency graph:
a
├── b
│ ├── d
│ ├── e
│ └── f
└── c
Whenever a node in the graph is updated,
all downstream nodes will be automatically updated via a webhook triggering Pulumi Deployments.
'''
project_var = "dependency-example"
organization = pulumi.get_organization()
f = auto_deploy.AutoDeployer("f",
organization=organization,
project=project_var,
stack="f",
downstream_refs=[])
e = auto_deploy.AutoDeployer("e",
organization=organization,
project=project_var,
stack="e",
downstream_refs=[])
d = auto_deploy.AutoDeployer("d",
organization=organization,
project=project_var,
stack="d",
downstream_refs=[])
c = auto_deploy.AutoDeployer("c",
organization=organization,
project=project_var,
stack="c",
downstream_refs=[])
b = auto_deploy.AutoDeployer("b",
organization=organization,
project=project_var,
stack="b",
downstream_refs=[
d.ref,
e.ref,
f.ref,
])
a = auto_deploy.AutoDeployer("a",
organization=organization,
project=project_var,
stack="a",
downstream_refs=[
b.ref,
c.ref,
])
package main
import (
"github.com/pulumi/pulumi-auto-deploy/sdk/go/autodeploy"
"github.com/pulumi/pulumi/sdk/v3/go/pulumi"
)
func main() {
/**
*
* The following example configures automatic deployment of stacks with the following dependency graph:
a
├── b
│ ├── d
│ ├── e
│ └── f
└── c
* Whenever a node in the graph is updated,
* all downstream nodes will be automatically updated via a webhook triggering Pulumi Deployments.
*/
pulumi.Run(func(ctx *pulumi.Context) error {
projectVar := "dependency-example"
organization := "pulumi"
f, err := autodeploy.NewAutoDeployer(ctx, "f", &autodeploy.AutoDeployerArgs{
Organization: pulumi.String(organization),
Project: pulumi.String(projectVar),
Stack: pulumi.String("f"),
DownstreamRefs: pulumi.StringArray{},
})
if err != nil {
return err
}
e, err := autodeploy.NewAutoDeployer(ctx, "e", &autodeploy.AutoDeployerArgs{
Organization: pulumi.String(organization),
Project: pulumi.String(projectVar),
Stack: pulumi.String("e"),
DownstreamRefs: pulumi.StringArray{},
})
if err != nil {
return err
}
d, err := autodeploy.NewAutoDeployer(ctx, "d", &autodeploy.AutoDeployerArgs{
Organization: pulumi.String(organization),
Project: pulumi.String(projectVar),
Stack: pulumi.String("d"),
DownstreamRefs: pulumi.StringArray{},
})
if err != nil {
return err
}
c, err := autodeploy.NewAutoDeployer(ctx, "c", &autodeploy.AutoDeployerArgs{
Organization: pulumi.String(organization),
Project: pulumi.String(projectVar),
Stack: pulumi.String("c"),
DownstreamRefs: pulumi.StringArray{},
})
if err != nil {
return err
}
b, err := autodeploy.NewAutoDeployer(ctx, "b", &autodeploy.AutoDeployerArgs{
Organization: pulumi.String(organization),
Project: pulumi.String(projectVar),
Stack: pulumi.String("b"),
DownstreamRefs: pulumi.StringArray{
d.Ref,
e.Ref,
f.Ref,
},
})
if err != nil {
return err
}
_, err = autodeploy.NewAutoDeployer(ctx, "a", &autodeploy.AutoDeployerArgs{
Organization: pulumi.String(organization),
Project: pulumi.String(projectVar),
Stack: pulumi.String("a"),
DownstreamRefs: pulumi.StringArray{
b.Ref,
c.Ref,
},
})
if err != nil {
return err
}
return nil
})
}
name: auto-deploy-demo
runtime: yaml
description: A simple auto-deploy example
variables:
project: dependency-example
# TODO: update once https://github.com/pulumi/pulumi-yaml/issues/461 is fixed
organization: pulumi
resources:
f:
type: auto-deploy:AutoDeployer
properties:
organization: ${organization}
project: ${project}
stack: f
downstreamRefs: []
e:
type: auto-deploy:AutoDeployer
properties:
organization: ${organization}
project: ${project}
stack: e
downstreamRefs: []
d:
type: auto-deploy:AutoDeployer
properties:
organization: ${organization}
project: ${project}
stack: d
downstreamRefs: []
c:
type: auto-deploy:AutoDeployer
properties:
organization: ${organization}
project: ${project}
stack: c
downstreamRefs: []
b:
type: auto-deploy:AutoDeployer
properties:
organization: ${organization}
project: ${project}
stack: b
downstreamRefs:
- ${d.ref}
- ${e.ref}
- ${f.ref}
a:
type: auto-deploy:AutoDeployer
properties:
organization: ${organization}
project: ${project}
stack: a
downstreamRefs:
- ${b.ref}
- ${c.ref}
Thank you for your feedback!
If you have a question about how to use Pulumi, reach out in Community Slack.
Open an issue on GitHub to report a problem or suggest an improvement.