Drift detection
Drift detection is the process of identifying changes in the actual state of your cloud environment that deviate from the expected state stored in Pulumi Cloud. This deviation can occur for various reasons, including manual adjustments made directly in the cloud provider’s console, unintended consequences of scripts, or unauthorized changes.
To use drift detection and remediation with Pulumi Deployments, you must first configure the deployment settings for your stack.
You can also run a remediate drift operation, which will run a pulumi up --refresh to treat the Pulumi program as the source of truth and override what is in the cloud.
Running Drift Detection from the CLI
Any preview of a refresh is considered a drift detection run in Pulumi Cloud. Running Drift Detection from the CLI is as simple as running pulumi refresh --preview-only or even just pulumi refresh, which will first run a preview (thereby creating the drift run), before running the actual refresh.
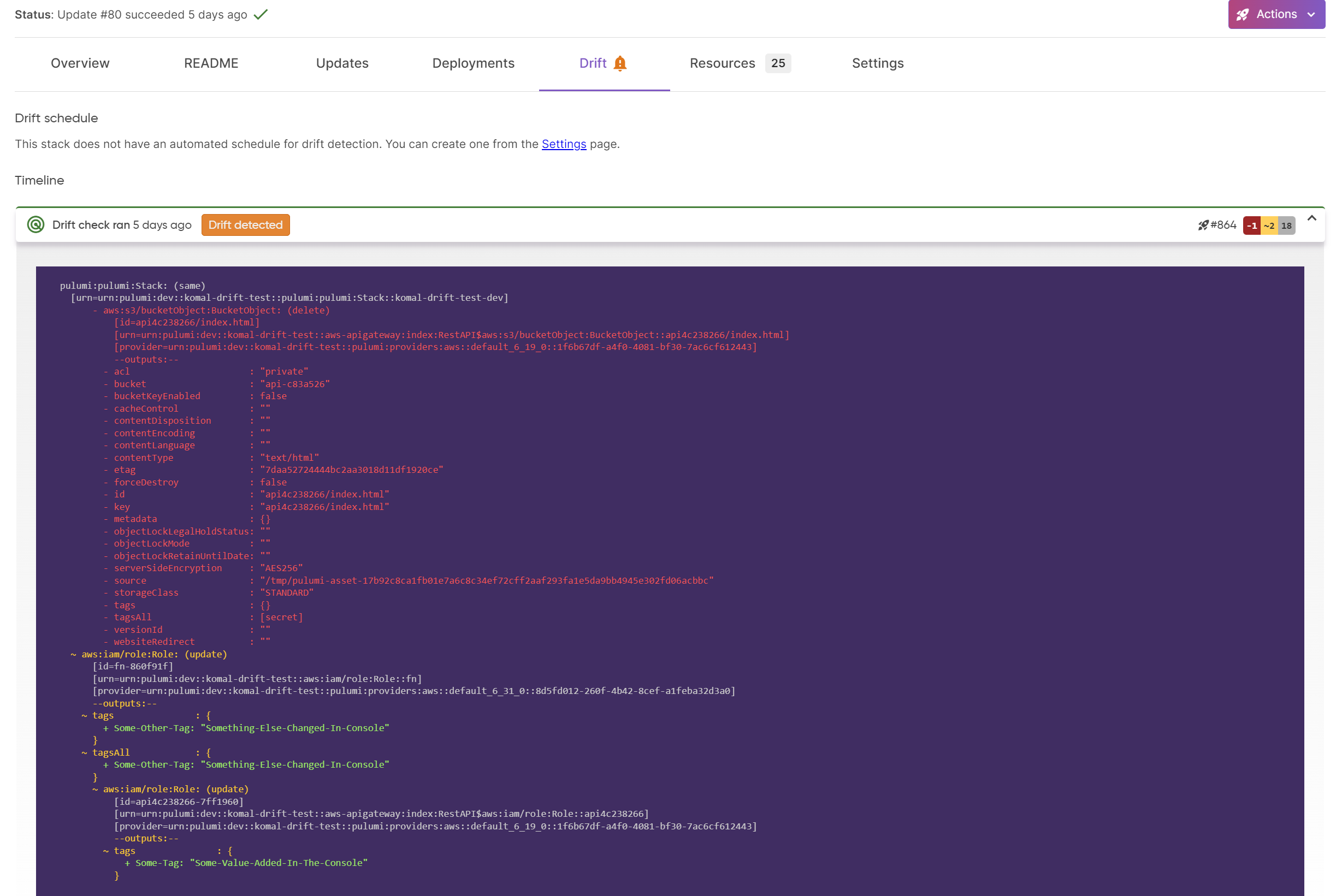
After your run completes you can see the drift run via the Drift tab for your stack.
Pulumi Cloud UI
Running via Click to Deploy
You can run a drift or remediate drift run ad hoc using the Click to Deploy option from your stack.
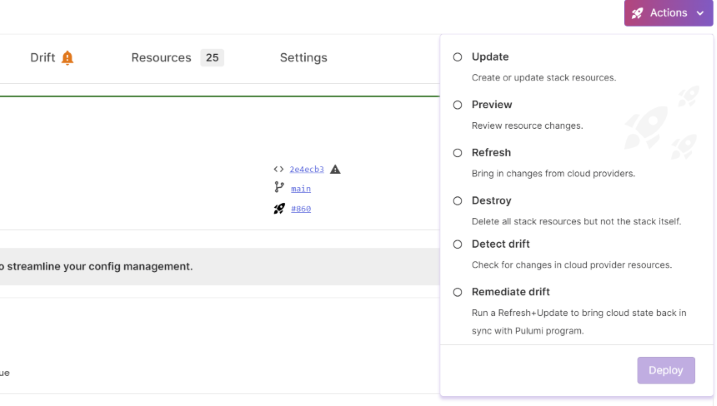
Drift tab
We’ve added a new Drift tab to the stack page. If the stack is currently in a drifted state, a warning bell icon will appear on the tab.
Regardless of how a drift run is initiated, all results will appear in this tab. If there is drift detected for a run, a diff summary of the changes will be included in the information card.
Configuring Drift Detection on a schedule
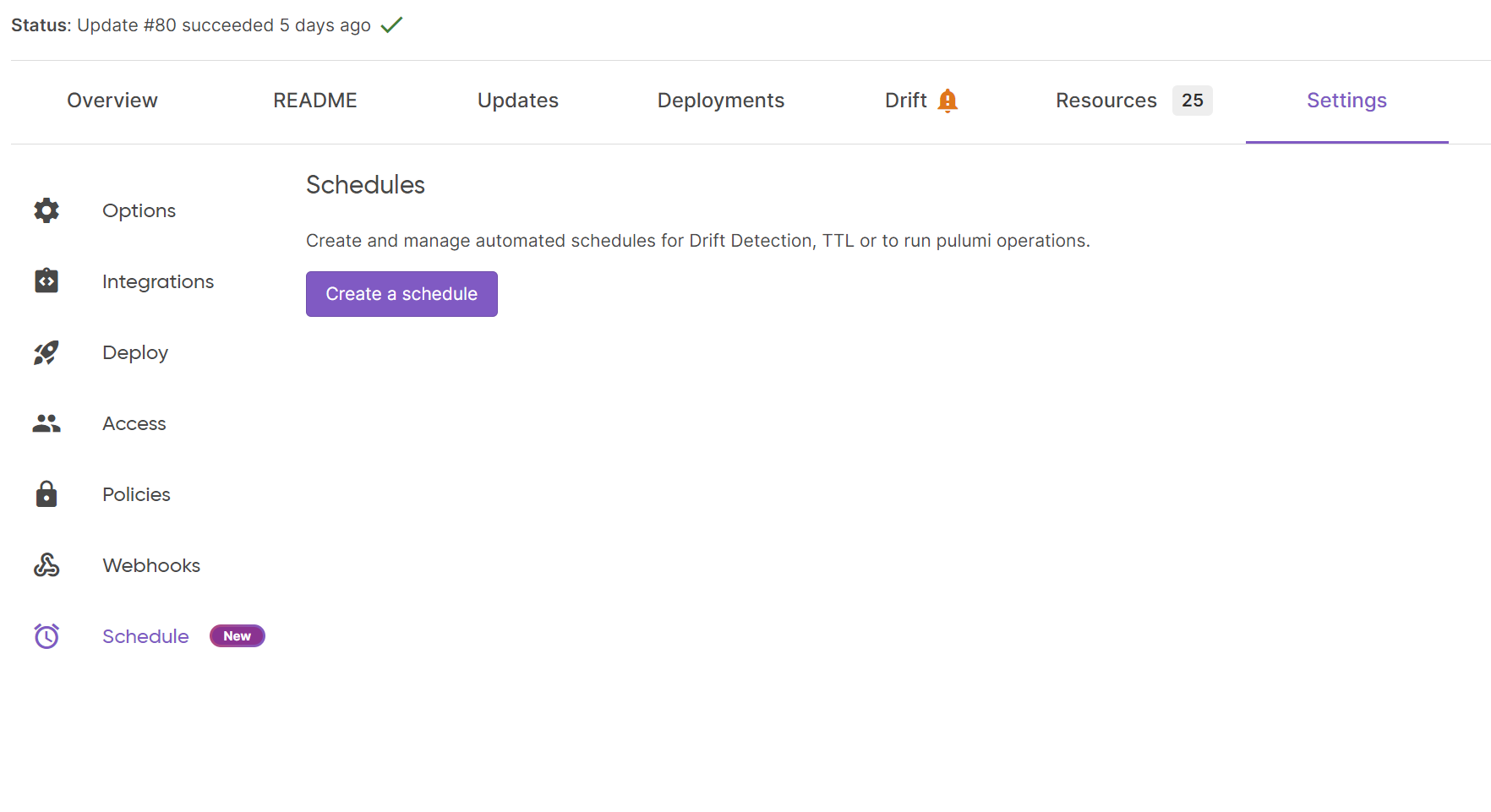
In order to set up Drift Detection and Remediation in the Pulumi Cloud console, follow these steps:
- Ensure Deployments Settings are configured on the stack see the docs
- Navigate to the Stack > Settings > Schedules
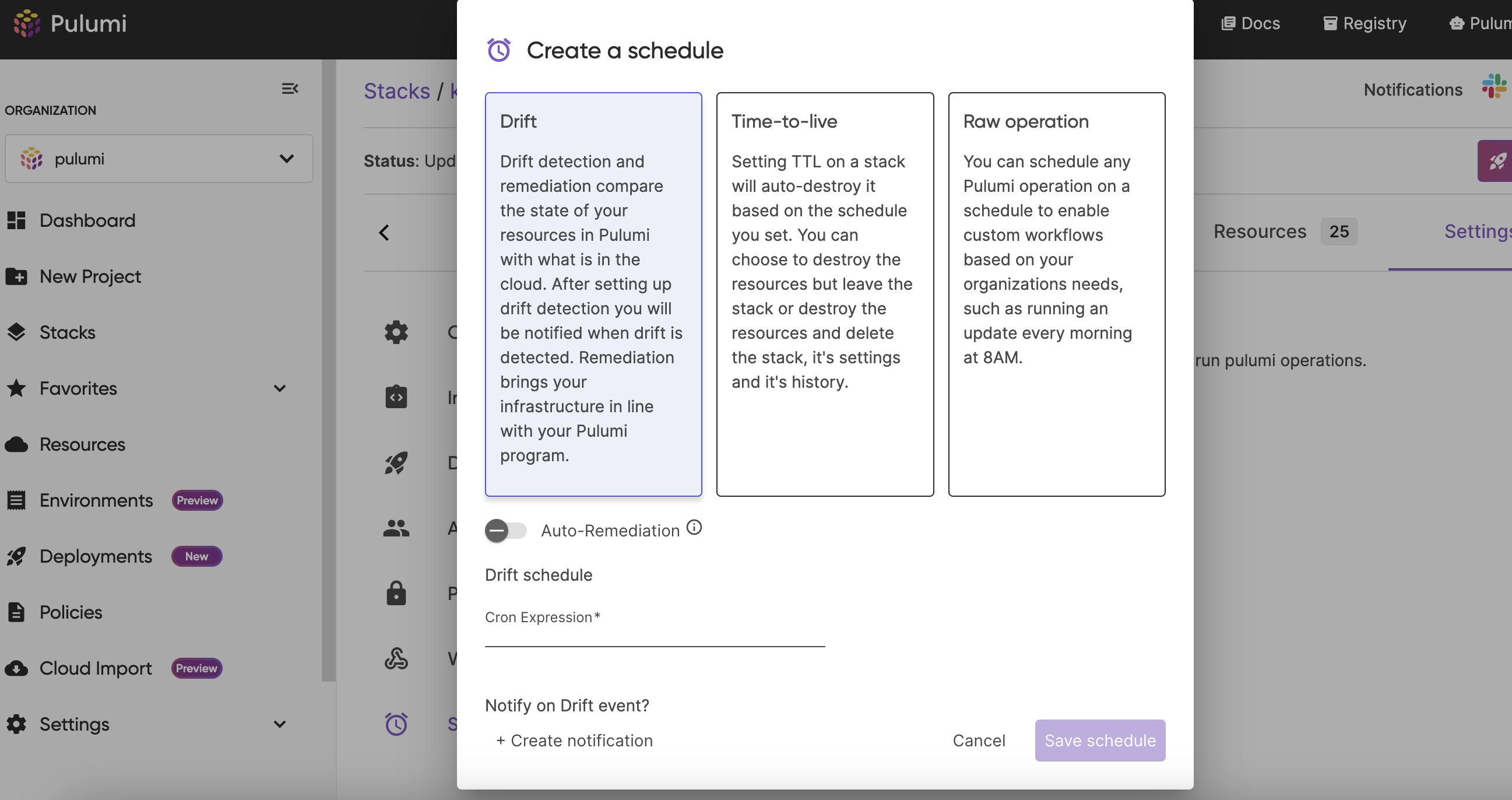
- Select “Drift”
- (Optional) Turn on auto-remediation if applicable
- Set the schedule using a cron expression
- Save the Schedule
Configuring notifications for Drift Detection
You can integrate Drift notifications to Slack, MS Teams, and more using Pulumi Webhooks integration.
- Navigate to the Stack > Settings > Webhooks.
- Select your desired Webhook format.
- Give your webhook a Display name, destination URL and optional secret.
- All events will include drift events, but you can also filter the events to Drift events:
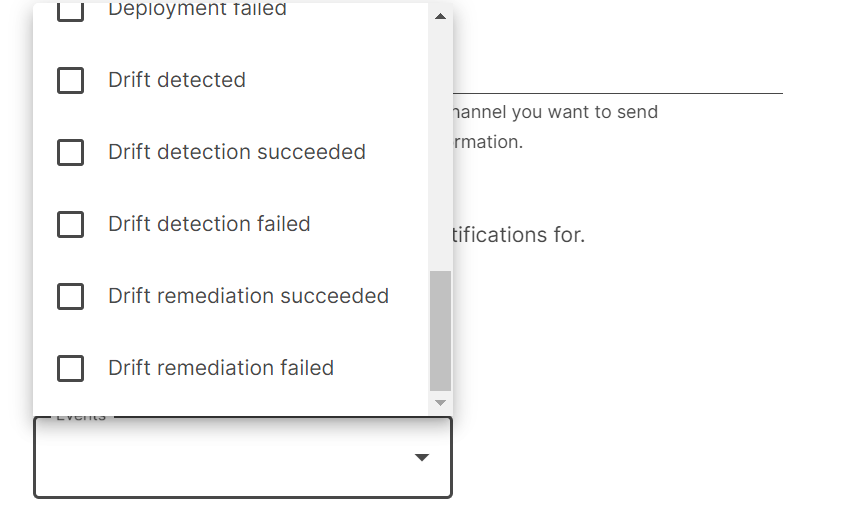
Summary of Drift Detection and Remediation events
- Drift detected - A drift run detected drift.
- Drift detection succeeded - A drift run succeeded, regardless of whether it detected drift or not.
- Drift detection failed - A drift run failed to finish.
- Drift remediation succeeded - A drift remediation run succeeded.
- Drift remediation failed - A drift remediation run failed to finish.
Setting it up via the REST API
For those who prefer to automate and script their infrastructure tasks, Drift Detection and Remediation can be configured programmatically using simple HTTP requests. Here are the new endpoints we have added:
- Create a drift schedule
- Get a drift schedule
- Update or delete a drift schedule
- Pause or resume a drift schedule
- List all schedules (includes raw Pulumi operations and Time-to-Live schedules)
Below is an example of setting up Drift Detection and Remediation on a stack, see the Pulumi Deployments REST API documentation for more details on how to set Drift Detection and Remediation up programmatically.
Create a Drift Detection and Remediation schedule:
curl -H "Accept: application/vnd.pulumi+json" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: token $PULUMI_ACCESS_TOKEN" \
--request POST \
--data '{"scheduleCron":"0 0 * * *","autoRemediate":true}' \
https://api.pulumi.com/api/stacks/{organization}/{project}/{stack}/deployments/drift/schedules
Setting it up via the Pulumi Service Provider
The Pulumi Service Provider allows you to set up automated Drift Detection and Remediation in source control.
import * as pulumi from "@pulumi/pulumi";
import * as pulumiservice from "@pulumi/pulumiservice";
const organizationName = "my-org";
const projectName = "my-project";
const stackName = "production";
// Creating a DriftSchedule for automatically running drift detection
const driftDetectionSchedule = new pulumiservice.DriftSchedule("driftDetectionSchedule", {
organization: organizationName,
project: projectName,
stack: stackName,
scheduleCron: "0 0 * * *", // Run drift detection daily at midnight
autoRemediate: true, // Automatically remediate any drift detected
});
export const driftScheduleId = driftDetectionSchedule.scheduleId;
import pulumi
import pulumi_pulumiservice as pulumiservice
organization_name = "my-org"
project_name = "my-project"
stack_name = "production"
# Create a drift detection schedule
drift_detection_schedule = pulumiservice.DriftSchedule("driftDetectionSchedule",
organization=organization_name,
project=project_name,
stack=stack_name,
schedule_cron="0 0 * * *", # Run drift detection daily at midnight
auto_remediate=True) # Automatically remediate any drift detected
pulumi.export('driftScheduleId', drift_detection_schedule.schedule_id)
package main
import (
"github.com/pulumi/pulumi-pulumiservice/sdk/go/pulumiservice"
"github.com/pulumi/pulumi/sdk/v3/go/pulumi"
)
func main() {
pulumi.Run(func(ctx *pulumi.Context) error {
driftDetectionSchedule, err := pulumiservice.NewDriftSchedule(ctx, "driftDetectionSchedule", &pulumiservice.DriftScheduleArgs{
Organization: pulumi.String("my-org"),
Project: pulumi.String("my-project"),
Stack: pulumi.String("production"),
ScheduleCron: pulumi.String("0 0 * * *"), // Run drift detection daily at midnight
AutoRemediate: pulumi.Bool(true), // Automatically remediate any drift detected
})
if err != nil {
return err
}
ctx.Export("driftScheduleId", driftDetectionSchedule.ScheduleId)
return nil
})
}
using Pulumi;
using PulumiService = Pulumi.PulumiService;
class Program
{
static Task<int> Main() => Deployment.RunAsync(() => {
var driftDetectionSchedule = new PulumiService.DriftSchedule("driftDetectionSchedule", new PulumiService.DriftScheduleArgs
{
Organization = "my-org",
Project = "my-project",
Stack = "production",
ScheduleCron = "0 0 * * *", // Run drift detection daily at midnight
AutoRemediate = true, // Automatically remediate any drift detected
});
return new Dictionary<string, object?>
{
{ "driftScheduleId", driftDetectionSchedule.ScheduleId }
};
});
}
import com.pulumi.Context;
import com.pulumi.Pulumi;
import com.pulumi.pulumiservice.Webhook;
import com.pulumi.pulumiservice.WebhookArgs;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Pulumi.run(App::stack);
}
private static void stack(Context ctx) {
var driftDetectionSchedule = new Webhook("driftDetectionSchedule", WebhookArgs.builder()
.organization("my-org")
.project("my-project")
.stack("production")
.scheduleCron("0 0 * * *") // Run drift detection daily at midnight
.autoRemediate(true) // Automatically remediate any drift detected
.build());
ctx.export("driftScheduleId", driftDetectionSchedule.scheduleId());
}
}
name: drift-detection-setup
runtime: yaml
description: Setup of automated drift detection with Pulumi
resources:
driftDetectionSchedule:
type: pulumiservice:index:DriftSchedule
properties:
organization: my-org
project: my-project
stack: production
scheduleCron: "0 0 * * *" # Run drift detection daily at midnight
autoRemediate: true # Automatically remediate any drift detected
outputs:
driftScheduleId: ${driftDetectionSchedule.scheduleId}
See the Pulumi Service Provider documentation for more details on how to manage Drift Detection and Remediation in source control.
Thank you for your feedback!
If you have a question about how to use Pulumi, reach out in Community Slack.
Open an issue on GitHub to report a problem or suggest an improvement.
