Google Cloud Static Website
The Google Cloud Static Website template creates an infrastructure as code project in your favorite language that deploys an HTML website to Google Cloud Platform with Pulumi. It uses a Cloud Storage bucket for file storage, configures the storage account to host a website, and provisions a Global Address to route traffic to the CDN for lower latency and caching. The template generates a complete Pulumi program, including placeholder web content, to give you a working project out of the box that you can customize easily and extend to suit your needs.
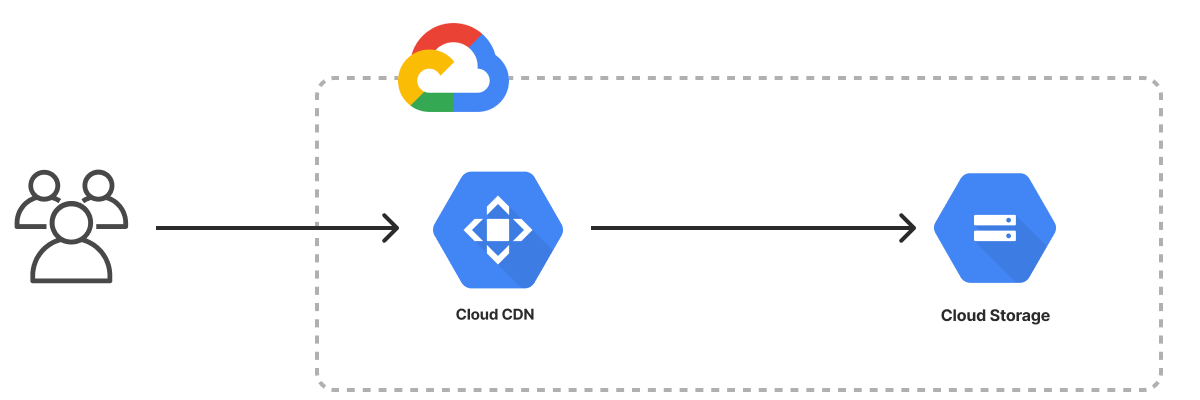
Using this template
To use this template to deploy a website of your own, make sure you’ve installed Pulumi and configured your Google Cloud credentials, then create a new project using the template in your language of choice:
$ mkdir my-site && cd my-site
$ pulumi new static-website-gcp-typescript
$ mkdir my-site && cd my-site
$ pulumi new static-website-gcp-python
$ mkdir my-site && cd my-site
$ pulumi new static-website-gcp-go
$ mkdir my-site && cd my-site
$ pulumi new static-website-gcp-csharp
$ mkdir my-site && cd my-site
$ pulumi new static-website-gcp-yaml
Follow the prompts to complete the new-project wizard. When it’s done, you’ll have a finished project that’s ready to deploy and configured with the most common settings. Feel free to inspect the code in index.jsindex.ts__main__.pymain.goProgram.csProgram.fsProgram.vbApp.javaPulumi.yaml
Deploying the project
The template requires no additional configuration. Once the new project is created, you can deploy it immediately with pulumi up:
$ pulumi up
When the deployment completes, Pulumi exports the following stack output values:
- originHostname
- The provider-assigned hostname of the Google Cloud Storage bucket.
- originURL
- The fully-qualified HTTP URL of the storage bucket endpoint.
- cdnHostname
- The provider-assigned hostname of the Google Cloud CDN. Useful for creating
CNAMErecords to associate custom domains. - cdnURL
- The fully-qualified HTTP URL of the Google Cloud CDN.
Output values like these are useful in many ways, most commonly as inputs for other stacks or related cloud resources. The computed cdnURL, for example, can be used from the command line to open the newly deployed website in your favorite web browser:
$ open $(pulumi stack output cdnURL)
Customizing the project
Projects created with the Static Website template expose the following configuration settings:
- path
- The path to the folder containing the files of the website. Defaults to
www, which is the name (and relative path) of the folder included with the template. - indexDocument
- The file to use for top-level pages. Defaults to
index.html. - errorDocument
- The file to use for error pages. Defaults to
error.html.
All of these settings are optional and may be adjusted either by editing the stack configuration file directly (by default, Pulumi.dev.yaml) or by changing their values with pulumi config set as shown below.
Using your own web content
If you already have a static website you’d like to deploy on Google Cloud Platform with Pulumi, you can do so either by replacing placeholder content in the www folder or by configuring the stack to point to another folder on your computer with the path setting:
$ pulumi config set path ../my-existing-website/build
$ pulumi up
Tidying up
You can cleanly destroy the stack and all of its infrastructure with pulumi destroy:
$ pulumi destroy
Learn more
Congratulations! You’re now well on your way to managing a production-grade static website on Google Cloud with Pulumi — and there’s lots more you can do from here:
- Discover more architecture templates in Templates →
- Dive into the Google Cloud Classic package by exploring the API docs in the Registry →
- Expand your understanding of how Pulumi works in Learn Pulumi →
- Read up on the latest new features in the Pulumi Blog →
