Introducing AWS CDK on Pulumi
Posted on
One of our key goals with Pulumi’s Universal Infrastructure as Code platform is to offer access to the widest range of cloud infrastructure building blocks for use within your cloud engineering projects. Over the years, that has led us to support interoperating seamlessly with a variety of alternative infrastructure definition formats, like Helm, CloudFormation, Azure Resource Manager and Kubernetes YAML. Today we’re really excited to add support for AWS CDK constructs to the list!
The AWS Cloud Development Kit (CDK) offers a large collection of higher-level libraries (“constructs”) for working with the AWS platform, built by service teams at AWS and by the AWS CDK community. These libraries are available in the same set of general purpose programming languages that Pulumi supports, with the primary difference being that AWS CDK compiles infrastructure programs into CloudFormation. This dependence on CloudFormation limits AWS CDK to being deployed via the CloudFormation deployment service which can slow down deployments and introduce some developer productivity friction due to the impedance mismatch between the program you write and the YAML it gets transpiled into.
With the new AWS CDK on Pulumi project, available in public preview today, we are opening up the ability to use AWS CDK constructs from within a Pulumi deployment. For users already using AWS CDK, this provides Pulumi as a new option for orchestrating deployments in place of CloudFormation, offering improved deployment speed, integration with the full set of features of the Pulumi Cloud Engineering Platform (like Policy as Code, Audit Logs, Secrets, and much more). And for Pulumi users, they are now able to leverage and benefit from the decades of experience AWS teams and the AWS CDK community have invested in designing well-architected infrastructure patterns through these constructs.
Even better, you can also now combine AWS CDK and Pulumi resources in a single Pulumi infrastructure as code project - passing outputs from Pulumi resources into AWS CDK constructs, and outputs from AWS CDK constructs into Pulumi resources. This allows you to work across the more than 80 cloud and SaaS providers that Pulumi offers access to, while still benefiting from high level libraries from the AWS CDK project, and without the hassles of a transpiler.
Deploying AWS CDK Constructs with Pulumi
To deploy existing AWS CDK Constructs using Pulumi, simply do the following:
- Create a class that derives from
pulumicdk.Stack(which itself is derived fromawscdk.Stack). - In the constructor, use any AWS CDK constructs from existing libraries such as
aws-cdk-lib - Call
this.synth()to finalize the stack and deploy its resources.
Constructing an instance of this pulumicdk.Stack from within your Pulumi program will then deploy all of the infrastructure defined by the CDK constructs in the Stack using Pulumi.
For example, the following program deploys two AWS CDK Constructs using Pulumi.
import * as fs from 'fs';
import * as events from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-events';
import * as events_targets from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-events-targets';
import * as lambda from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-lambda';
import { Duration } from 'aws-cdk-lib';
import * as pulumicdk from '@pulumi/cdk';
import { remapCloudControlResource } from './adapter';
class LambdaStack extends pulumicdk.Stack {
constructor(id: string, options?: pulumicdk.StackOptions) {
super(id, { ...options, remapCloudControlResource });
// Use the AWS CDK Lambda Function API directly.
const lambdaFn = new lambda.Function(this, 'lambda', {
code: new lambda.InlineCode(fs.readFileSync('lambda-handler.py', { encoding: 'utf-8' })),
handler: 'index.main',
timeout: Duration.seconds(300),
runtime: lambda.Runtime.PYTHON_3_6,
});
// Use the AWS CDK Rule API directly.
const rule = new events.Rule(this, 'rule', {
// Run 6:00 PM UTC every Monday through Friday
schedule: events.Schedule.expression('cron(0 18 ? * MON-FRI *)'),
});
// Use the AWS CDK to add a Rule target to trigger the Function.
rule.addTarget(new events_targets.LambdaFunction(lambdaFn));
// Finalize the stack and deploy its resources.
this.synth();
}
}
const stack = new LambdaStack('teststack');
This can be deployed with the pulumi CLI just like any other Pulumi program.
> pulumi up
Updating (dev)
View Live: https://app.pulumi.com/lukehoban/cdk-cron-lambda/dev/updates/37
Type Name Status
+ pulumi:pulumi:Stack cdk-cron-lambda-dev created
+ └─ cdk:index:Stack teststack created
+ └─ cdk:construct:LambdaStack teststack/teststack created
+ ├─ cdk:construct:Function teststack/teststack/lambda created
+ │ ├─ cdk:construct:Role teststack/teststack/lambda/ServiceRole created
+ │ │ └─ aws-native:iam:Role lambdaServiceRole494E4CA6 created
+ │ └─ aws-native:lambda:Function lambda8B5974B5 created
+ └─ cdk:construct:Rule teststack/teststack/rule created
+ ├─ aws:cloudwatch:EventRule ruleF2C1DCDC created
+ ├─ aws:cloudwatch:EventTarget Target0 created
+ └─ aws:lambda:Permission ruleAllowEventRuleteststacklambda47768855D6EFF36B created
Resources:
+ 11 created
Duration: 48s
We can see that each CDK Construct is shown in the Pulumi resource tree, and the leaf nodes of the deployment are the underlying AWS resources needed for this cloud infrastructure. Note that they are deployed via Pulumi, not via CloudFormation. This enables faster deployments, because Pulumi coordinates directly with AWS instead of going through CloudFormation, as well as the ability to use Pulumi features like pulumi logs, Policy as Code, and the features of the Pulumi Service.
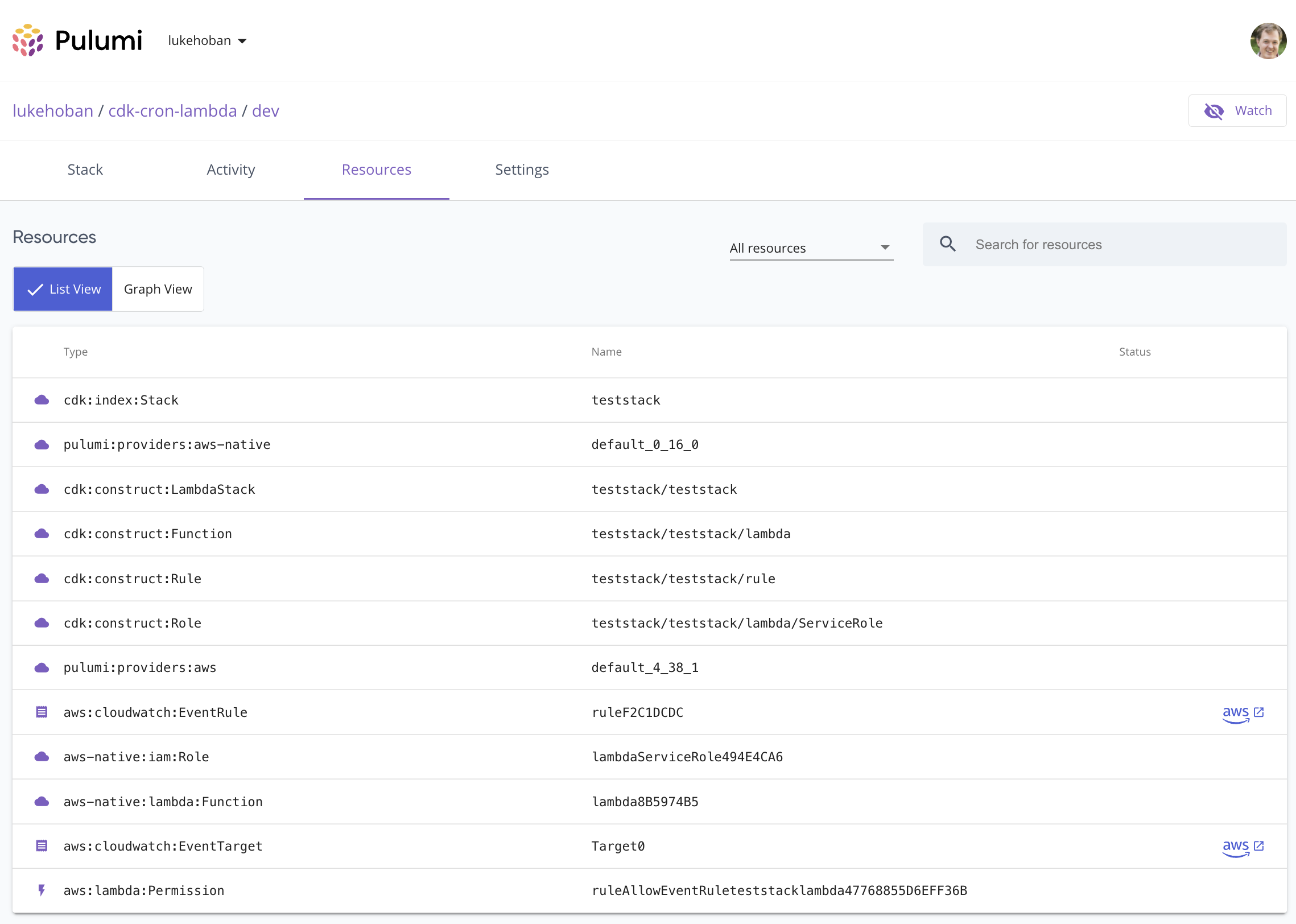
Using AWS CDK Constructs Within Pulumi Programs
We can also combine the best of AWS CDK with the best of Pulumi, by using both Pulumi resources and AWS CDK Constructs in the same deployment. This enables combining rich AWS CDK Constructs with the breadth of the Pulumi ecosystem, including support for multiple cloud and SaaS providers.
The following example shows creating an AWS Lambda Function with the Pulumi AWS SDK, and then using an output of that Function (the arn) as an input to an AWS Events Rule CDK Construct. An output from the AWS CDK Construct is then converted to a Pulumi Output value which can be used in the rest of the Pulumi program - and in particular as a Pulumi Stack Output.
import * as events from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-events';
import * as events_targets from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-events-targets';
import * as lambda from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-lambda';
import * as pulumi from '@pulumi/pulumi';
import * as pulumicdk from '@pulumi/cdk';
import * as aws from '@pulumi/aws';
import { remapCloudControlResource } from './adapter';
// Create a resource in Pulumi
const fn = new aws.lambda.CallbackFunction('lambda', {
callback: (ev, ctx) => console.log(JSON.stringify(ev)),
});
class LambdaStack extends pulumicdk.Stack {
ruleArn: pulumi.Output<string>;
constructor(id: string, options?: pulumicdk.StackOptions) {
super(id, { ...options, remapCloudControlResource });
// Use the AWS CDK Rule API directly.
const rule = new events.Rule(this, 'rule', {
// Run 6:00 PM UTC every Monday through Friday
schedule: events.Schedule.expression('cron(0 18 ? * MON-FRI *)'),
});
// Get an AWS CDK Function instance from the Pulumi Lambda ARN.
const lambdaFn = lambda.Function.fromFunctionArn(this, 'lambdaFn', pulumicdk.asString(fn.arn));
// Use the AWS CDK to add a Rule target to trigger the Function.
rule.addTarget(new events_targets.LambdaFunction(lambdaFn));
// Export the Lambda function's ARN as an output.
this.ruleArn = this.asOutput(rule.ruleArn);
this.synth();
}
}
const stack = new LambdaStack('teststack');
export const ruleArn = stack.ruleArn;
Note how the pulumicdk.asString and asOutput functions are used to convert Pulumi Outputs to AWS CDK Tokens and vice-versa to map values out of and into Pulumi.
Building on AWS Native and the AWS Cloud Control API
Last year we released a new AWS Native Pulumi provider in preview. The AWS Native provider builds on the new AWS Cloud Control API, which offers direct provisioning support for the same resource model supported by AWS CloudFormation.
The new AWS CDK on Pulumi builds upon AWS Native by converting the CloudFormation resource tree into the corresponding resource definitions from the AWS Native provider. This provides a high fidelity mapping of each resource into Pulumi. The coverage provided by AWS Cloud Control API (and thus AWS Native) is not yet complete across the entire breadth of the CloudFormation resource model though, so for some resources, it may be necessary to map them to a resource definition to use via the AWS provider. This is handled via the remapCloudControlResource API which allows providing a custom mapping for a given CloudFormation resource type which is not yet supported in Pulumi AWS Native and AWS Cloud Control.
For example, to provide a mapping for the AWS::Lambda::Permission resource type, define a function like the following:
export function remapCloudControlResource(
element: CfnElement,
logicalId: string,
typeName: string,
rawProps: any,
options: pulumi.ResourceOptions,
): pulumi.CustomResource | undefined {
const props = pulumicdk.interop.normalize(rawProps);
switch (typeName) {
case 'AWS::Lambda::Permission':
return new aws.lambda.Permission(
logicalId,
{
action: props['action'],
function: props['functionName'],
principal: props['principal'],
sourceArn: props['sourceArn'] ?? undefined,
},
options,
);
}
return undefined;
}
In many cases, this is not needed, as AWS CDK on Pulumi offers builtin support for remapping many common resources. Over the coming months, as AWS Cloud Control API support expands to cover more of the CloudFormation resource model, these remappings will become less necessary in practice, with almost all resources being supported directly via Pulumi AWS Native.
Using High-Level “L3” Constructs
AWS CDK offers a mix of relatively low level (unopinionated) constructs, as well as high level (more opinionated) constructs. With AWS CDK on Pulumi, we can use any of these. This includes libraries like aws-ecs-patterns and AWS Solutions Constructs.
For example, to deploy a load balanced and auto-scaled Fargate service to a dedicated VPC, we can use the following program:
import * as ec2 from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-ec2';
import * as pulumi from '@pulumi/pulumi';
import * as pulumicdk from '@pulumi/cdk';
import * as ecs from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-ecs';
import * as ecs_patterns from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-ecs-patterns';
import { Construct } from 'constructs';
import { Stack, Duration, CfnOutput } from 'aws-cdk-lib';
import {remapCloudControlResource } from './adapter';
class FargateStack extends pulumicdk.Stack {
loadBalancerDNS: pulumi.Output<string>;
constructor(id: string, options?: pulumicdk.StackOptions) {
super(id, { ...options, remapCloudControlResource });
// Create VPC and Fargate Cluster
const vpc = new ec2.Vpc(this, 'MyVpc', { maxAzs: 2 });
const cluster = new ecs.Cluster(this, 'fargate-service-autoscaling', { vpc });
// Create Fargate Service
const fargateService = new ecs_patterns.NetworkLoadBalancedFargateService(this, 'sample-app', {
cluster,
taskImageOptions: {
image: ecs.ContainerImage.fromRegistry("amazon/amazon-ecs-sample")
},
});
// Setup AutoScaling policy
const scaling = fargateService.service.autoScaleTaskCount({ maxCapacity: 2 });
scaling.scaleOnCpuUtilization('CpuScaling', {
targetUtilizationPercent: 50,
scaleInCooldown: Duration.seconds(60),
scaleOutCooldown: Duration.seconds(60)
});
this.loadBalancerDNS = this.asOutput(fargateService.loadBalancer.loadBalancerDnsName);
// Finalize the stack and deploy its resources.
this.synth();
}
};
const stack = new FargateStack('fargatestack');
export const loadBalancerURL = stack.loadBalancerDNS;
Deploying this with pulumi up builds a few dozen AWS resources to construct the various building blocks necessary to capture this in raw AWS infrastructure:
> pulumi up
Updating (dev)
View Live: https://app.pulumi.com/lukehoban/pulumi-aws-cdk-fargate/dev/updates/1
Type Name Status
+ pulumi:pulumi:Stack pulumi-aws-cdk-fargate-dev created
+ └─ cdk:index:Stack fargatestack created
+ └─ cdk:construct:FargateStack fargatestack/fargatestack created
+ ├─ cdk:construct:Cluster fargatestack/fargatestack/fargate-service-autoscaling created
+ │ └─ aws-native:ecs:Cluster fargateserviceautoscalingD107CF93 created
+ ├─ cdk:construct:NetworkLoadBalancedFargateService fargatestack/fargatestack/sample-app created
+ │ ├─ cdk:construct:FargateTaskDefinition fargatestack/fargatestack/sample-app/TaskDef created
+ │ │ ├─ cdk:construct:ContainerDefinition fargatestack/fargatestack/sample-app/TaskDef/web created
+ │ │ │ └─ cdk:construct:LogGroup fargatestack/fargatestack/sample-app/TaskDef/web/LogGroup created
+ │ │ │ └─ aws-native:logs:LogGroup sampleappTaskDefwebLogGroup34BE8C79 created
+ │ │ ├─ cdk:construct:Role fargatestack/fargatestack/sample-app/TaskDef/ExecutionRole created
+ │ │ │ ├─ cdk:construct:Policy fargatestack/fargatestack/sample-app/TaskDef/ExecutionRole/DefaultPolicy created
+ │ │ │ │ ├─ aws:iam:Policy sampleappTaskDefExecutionRoleDefaultPolicy0AD15374 created
+ │ │ │ │ └─ aws:iam:RolePolicyAttachment sampleappTaskDefExecutionRoleDefaultPolicy0AD15374-0 created
+ │ │ │ └─ aws-native:iam:Role sampleappTaskDefExecutionRoleAD6F4C40 created
+ │ │ ├─ cdk:construct:Role fargatestack/fargatestack/sample-app/TaskDef/TaskRole created
+ │ │ │ └─ aws-native:iam:Role sampleappTaskDefTaskRoleB530CAC0 created
+ │ │ └─ aws-native:ecs:TaskDefinition sampleappTaskDef6BF75736 created
+ │ ├─ cdk:construct:NetworkLoadBalancer fargatestack/fargatestack/sample-app/LB created
+ │ │ ├─ cdk:construct:NetworkListener fargatestack/fargatestack/sample-app/LB/PublicListener created
+ │ │ │ ├─ cdk:construct:NetworkTargetGroup fargatestack/fargatestack/sample-app/LB/PublicListener/ECSGroup created
+ │ │ │ │ └─ aws:lb:TargetGroup sampleappLBPublicListenerECSGroup525A567D created
+ │ │ │ └─ aws-native:elasticloadbalancingv2:Listener sampleappLBPublicListenerC4DF6480 created
+ │ │ └─ aws:lb:LoadBalancer sampleappLBBDE1D276 created
+ │ └─ cdk:construct:FargateService fargatestack/fargatestack/sample-app/Service created
+ │ ├─ cdk:construct:ScalableTaskCount fargatestack/fargatestack/sample-app/Service/TaskCount created
+ │ │ └─ cdk:construct:ScalableTarget fargatestack/fargatestack/sample-app/Service/TaskCount/Target created
+ │ │ ├─ cdk:construct:TargetTrackingScalingPolicy fargatestack/fargatestack/sample-app/Service/TaskCount/Target/CpuScaling created
+ │ │ │ └─ aws:appautoscaling:Policy sampleappServiceTaskCountTargetCpuScalingF4452F80 created
+ │ │ └─ aws:appautoscaling:Target sampleappServiceTaskCountTargetE827DC30 created
+ │ ├─ cdk:construct:SecurityGroup fargatestack/fargatestack/sample-app/Service/SecurityGroup created
+ │ │ └─ aws:ec2:SecurityGroup sampleappServiceSecurityGroup0ABF0D21 created
+ │ └─ aws-native:ecs:Service sampleappServiceE7504FDB created
+ └─ cdk:construct:Vpc fargatestack/fargatestack/MyVpc created
+ ├─ cdk:construct:PublicSubnet fargatestack/fargatestack/MyVpc/PublicSubnet2 created
+ │ ├─ aws:ec2:Eip MyVpcPublicSubnet2EIP8CCBA239 created
+ │ ├─ aws-native:ec2:Subnet MyVpcPublicSubnet2Subnet492B6BFB created
+ │ ├─ aws-native:ec2:RouteTable MyVpcPublicSubnet2RouteTable1DF17386 created
+ │ ├─ aws:ec2:NatGateway MyVpcPublicSubnet2NATGateway91BFBEC9 created
+ │ ├─ aws:ec2:Route MyVpcPublicSubnet2DefaultRoute052936F6 created
+ │ └─ aws-native:ec2:SubnetRouteTableAssociation MyVpcPublicSubnet2RouteTableAssociation227DE78D created
+ ├─ cdk:construct:PublicSubnet fargatestack/fargatestack/MyVpc/PublicSubnet1 created
+ │ ├─ aws:ec2:Eip MyVpcPublicSubnet1EIP096967CB created
+ │ ├─ aws-native:ec2:Subnet MyVpcPublicSubnet1SubnetF6608456 created
+ │ ├─ aws-native:ec2:RouteTable MyVpcPublicSubnet1RouteTableC46AB2F4 created
+ │ ├─ aws:ec2:NatGateway MyVpcPublicSubnet1NATGatewayAD3400C1 created
+ │ ├─ aws-native:ec2:SubnetRouteTableAssociation MyVpcPublicSubnet1RouteTableAssociation2ECEE1CB created
+ │ └─ aws:ec2:Route MyVpcPublicSubnet1DefaultRoute95FDF9EB created
+ ├─ cdk:construct:PrivateSubnet fargatestack/fargatestack/MyVpc/PrivateSubnet2 created
+ │ ├─ aws-native:ec2:RouteTable MyVpcPrivateSubnet2RouteTableCEDCEECE created
+ │ ├─ aws-native:ec2:Subnet MyVpcPrivateSubnet2Subnet0040C983 created
+ │ ├─ aws-native:ec2:SubnetRouteTableAssociation MyVpcPrivateSubnet2RouteTableAssociation86A610DA created
+ │ └─ aws:ec2:Route MyVpcPrivateSubnet2DefaultRoute9CE96294 created
+ ├─ cdk:construct:PrivateSubnet fargatestack/fargatestack/MyVpc/PrivateSubnet1 created
+ │ ├─ aws-native:ec2:RouteTable MyVpcPrivateSubnet1RouteTable8819E6E2 created
+ │ ├─ aws-native:ec2:Subnet MyVpcPrivateSubnet1Subnet5057CF7E created
+ │ ├─ aws-native:ec2:SubnetRouteTableAssociation MyVpcPrivateSubnet1RouteTableAssociation56D38C7E created
+ │ └─ aws:ec2:Route MyVpcPrivateSubnet1DefaultRouteA8CDE2FA created
+ ├─ aws-native:ec2:InternetGateway MyVpcIGW5C4A4F63 created
+ ├─ aws-native:ec2:VPC MyVpcF9F0CA6F created
+ └─ aws:ec2:InternetGatewayAttachment MyVpcVPCGW488ACE0D created
Outputs:
loadBalancerURL: "sampleappLBBDE1D276-f412396-b0bebc132ad72c07.elb.us-west-2.amazonaws.com"
Resources:
+ 61 created
Duration: 4m51s
Future Directions
Currently AWS CDK on Pulumi is supported only for TypeScript users, due to how the AWS CDK synthesis process (implemented in TypeScript) must be invoked from within the Pulumi program. We are exploring ways to bring this support into other Pulumi (and CDK) languages as part of future updates to the library.
In the meantime, AWS CDK on Pulumi can be used within Component Packages implemented in TypeScript, and exposed to any Pulumi language (including newly supported Java and YAML.
Summary
Support for deploying AWS CDK constructs from within Pulumi programs opens up a wide range of new opportunities to interoperate between the AWS CDK and Pulumi ecosystems.For existing AWS CDK users, this provides new ways to deploy your CDK infrastructure and constructs. For existing Pulumi users, this opens up new higher-level libraries from the AWS CDK to use from within your Pulumi programs. We’re excited to be bringing these two communities closer together, and can’t wait to see what cloud builders can do with these two great cloud technologies together.
The AWS CDK on Pulumi project is open source at https://github.com/pulumi/pulumi-cdk and on NPM at https://www.npmjs.com/package/@pulumi/cdk. Get started today!

