Welcoming GitLab users to Pulumi
Posted on
We are very pleased to announce that Pulumi now supports signing-in with your GitLab account. Don’t have an account on GitLab yet? Head on over to https://gitlab.com and sign-up for an account.
Why GitLab?
GitLab is a fully-integrated DevOps service that not only provides git repository management but also allows you to collaborate using issue boards, setup build and deployment pipelines. It provides an end-to-end solution that starts from your code and ends with your customers, all without ever having to leave GitLab.
And with Pulumi on GitLab, you truly never have to leave GitLab, not even to provision your infrastructure to run your services on the cloud.
Login and create a GitLab-backed Pulumi organization
Log into
app.pulumi.comusing the GitLab Sign-in.Click on the organizations dropdown menu and select Add an organization.
On the next page, you may select your GitLab group, based on which a Pulumi organization will be created.
Once the organization is created, you can create stacks in your newly created organization, so that other members of your organization can collaborate with you.
Inviting members in your GitLab group to use Pulumi
Select the organization you created from the organization dropdown menu. You should see a People tab. Select the People tab.
- You will see the People tab if you added the organization on Pulumi or if you are an Owner of the GitLab group on gitlab.com.
- Members must have an active and valid role in your GitLab group, so that you may invite them.
From the People tab, you can invite additional members in your group to also use Pulumi. By inviting members in your group to join Pulumi, you can collaborate with them more easily and share stacks, just like you would collaborate on a project on GitLab.
Running Pulumi on GitLab
Pulumi can be run in many CI/CD environments. Pulumi can be easily integrated in your CI pipeline on GitLab, too.
Deep-linking to your GitLab projects, branches and commits
When you run Pulumi in a GitLab-based repo, the pulumi CLI recognizes
the correct metadata based on your repository’s remote configuration
and uses that information to enhance your experience on
app.pulumi.com.
Here’s an example of a project hosted on gitlab.com.
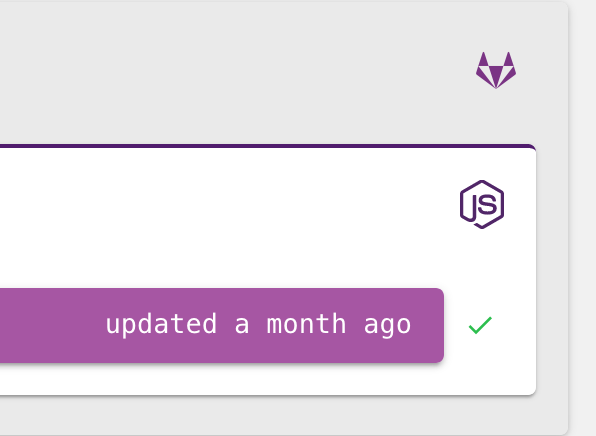
Here’s the same project with some activity having links to the commit-hash, and the branch in which this stack was updated.

FAQ
I use my GitHub identity to login into GitLab. How do I do that with Pulumi?
Click the GitLab sign-in button on <app.pulumi.com>, Pulumi will redirect you to gitlab.com where GitLab will present you with the sign-in options to login into your GitLab account. At that point, you may choose any of the sign-in options GitLab provides to sign-in.
I already have an account on Pulumi. Will signing-in with my GitLab identity create a new account?
Yes. Signing-in with a GitLab account will create a new account. That
means, your stacks and activity will stay with the other account. You
can migrate them by performing a
pulumi stack export
from your source stack and then importing it using
pulumi stack import
in a new stack in your GitLab-based account.
If you would like to add your GitLab identity to your existing Pulumi account, you can do so by connecting your GitLab identity from your Pulumi account’s profile page.
How do I login into the pulumi CLI on my local machine using my GitLab-backed Pulumi account?
One of the benefits of using <app.pulumi.com> is to track the state of
your stacks. When you are running the pulumi CLI on your machine, you
can login into your account by typing pulumi login. There are two
options for you to complete the login process. You can either create an
Access Token on <app.pulumi.com> or simply press ENTER to let the
CLI launch the browser.
If you would like to let the CLI launch the browser, ensure that you are already signed-in using GitLab at <app.pulumi.com> using your machine’s default browser. This way, when the browser is launched by the CLI, your Pulumi account based on your GitLab identity would be automatically used.

