Multicloud Kubernetes: Running Apps Across EKS, AKS, and GKE
Posted on
Kubernetes clusters from the managed platforms of AWS Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS), Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), and GCP Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) all vary in configuration, management, and resource properties. This variance creates unnecessary complexity in cluster provisioning and application deployments, as well as for CI/CD and testing.
Additionally, if you wanted to deploy the same app across multiple clusters for specific use cases or test scenarios across providers, subtleties such as LoadBalancer outputs and cluster connection settings can be a nuisance to manage.
In this post, we’ll see how to use Pulumi to deploy the kuard app across EKS,
AKS, GKE and a local Kubernetes cluster, such as Docker Desktop or a self-managed cluster.
We’ll spin up the clusters in each provider, launch the app,
and manage both cluster and app using the TypeScript programming language.
View the full example and code.
Cluster Provisioning
Provisioning Kubernetes clusters and their IaaS resources is made simple through Pulumi’s various SDKs for the cloud providers:
- AWS:
pulumi/eks - GCP:
pulumi/gcp - Azure:
pulumi/azure
Crosswalk for AWS further allows us to leverage the Pulumi
libraries of common infrastructure for AWS to simplify cloud resource
instantiation and management while gaining best-practices as defaults.
Check out the pulumi/awsx SDK to get
started.
For local clusters such as those that are self-managed, or provisioned by a
tool like Docker Desktop, Pulumi can still deploy workloads to these these
systems given that the pulumi/kubernetes workload SDK only requires a valid kubeconfig
file. For more information on Pulumi’s Kubernetes support, check out the Kubernetes reference page.
We will use the cloud SDKs to provision the managed Kubernetes clusters. Given that we’re working with real code, we are afforded developer benefits such as: code linting, type checking, IDE hints and completion, abstractions and inheritance.
Leveraging these development features creates the opportunity to encapsulate the finer-grained details and settings, and expose the capability to create clusters as simple as the following code:
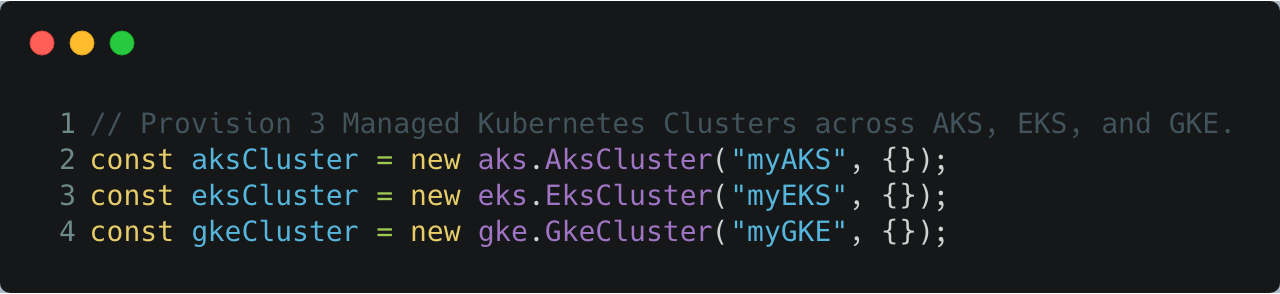
Workload Deployment
Once the clusters are provisioned, we can leverage the
pulumi/kubernetes SDK to manage the Kubernetes
workloads that will be deployed into the clusters.
The pulumi/kubernetes SDK uses the official Kubernetes client-go
library to interact with Kubernetes. Therefore, Pulumi can work pretty
much anywhere kubectl works, even if Pulumi was not used to create the cluster.
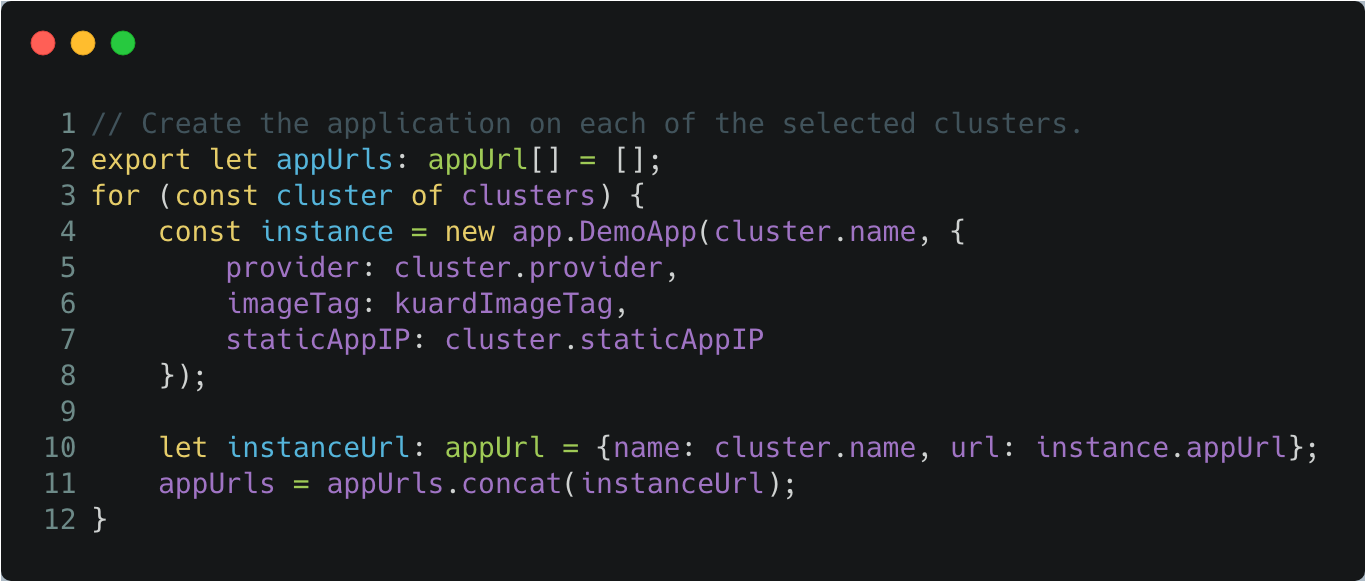
Summary
As shown in the code samples, it becomes relatively easy to provision and manage Kubernetes clusters across multiple clouds, as well as deploy workloads to the cluster regardless if they are managed by a cloud provider, or self-managed.
The various SDKS allow you to leverage industry standard best-practices and defaults, in addition to allowing you to further configure and customize how your clusters and apps are managed.
Testing apps across various providers in this form allows you to abstract away the details of provider specific implementations, and focus on how your app operates in the various contexts.
Learn More
If you’d like to learn about Pulumi and how to manage your infrastructure and Kubernetes multi-cloud capabilities through code, get started today. Pulumi is open source and free to use.
For further examples on how to use Pulumi to create Kubernetes clusters, or deploy workloads to a cluster, check out the rest of the Kubernetes tutorials.
As always, you can check out our code on GitHub, follow us on Twitter, subscribe to our YouTube channel, or join our Community Slack channel if you have any questions, need support, or just want to say hello.
If you’d like to chat with our team, or get hands-on assistance with migrating your existing configuration code to Pulumi, please don’t hesitate to drop us a line.
We also encourage you to watch Pulumi team member Levi Blackstone demo this post in an episode of the Kubernetes Community Meeting.

