How Pinpoint Manages Kubernetes Costs and Deployments

This guest blog was contributed by Andrew Kunzel and Michael Goode of Pinpoint. Andrew is the Director of Backend Engineering, and Michael is a Platform Operations Engineer.
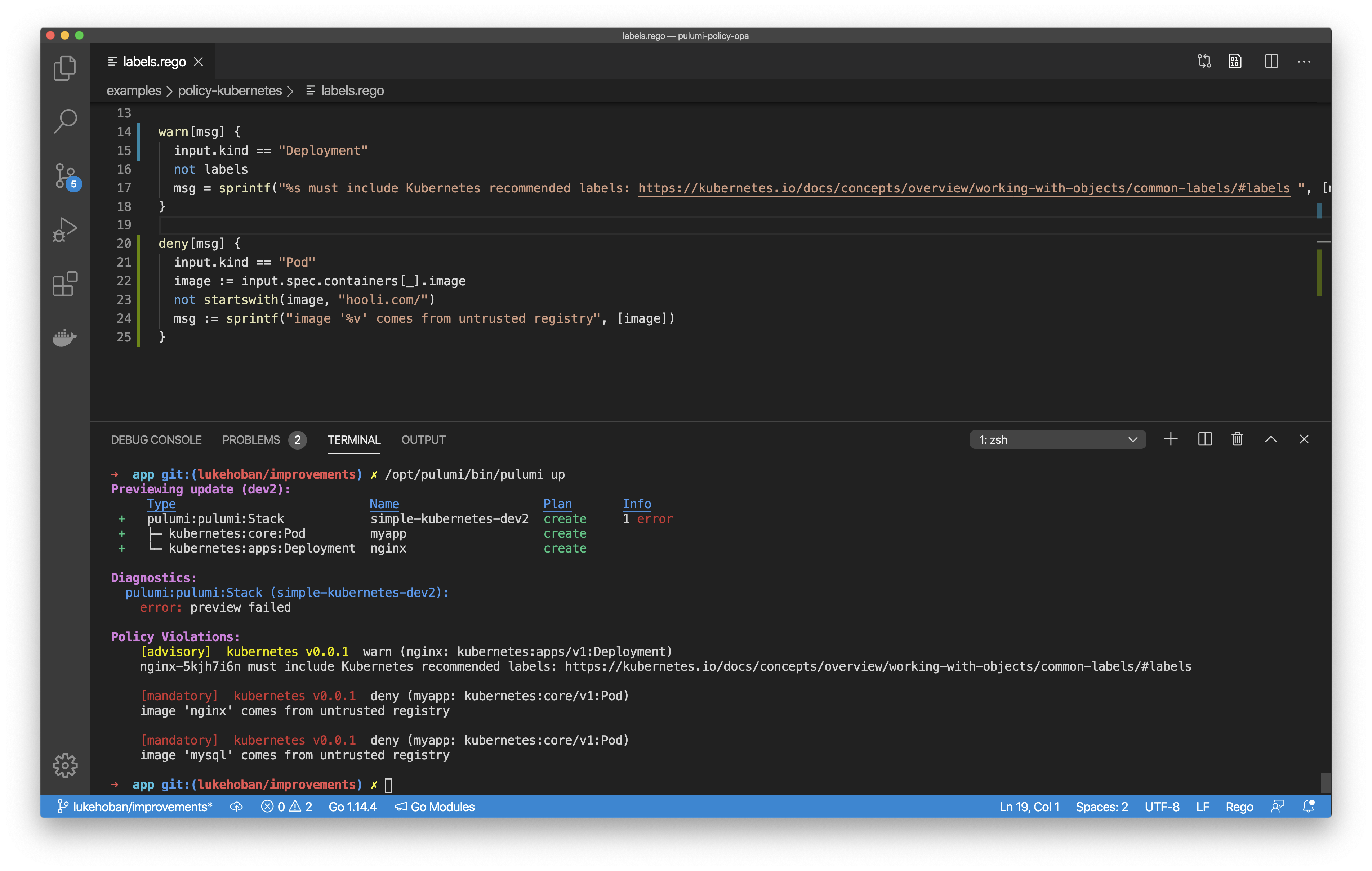
At Pinpoint, Kubernetes is the most powerful tool in our arsenal. It allows us to deploy and rapidly scale our applications with speed and efficiency that continues to delight our customers. In recent years, managed services like AWS EKS have made it easier than ever to leverage the power of Kubernetes in even the smallest of organizations. Yet even with these new conveniences, managing all of this infrastructure can be a daunting task. Right out of the gate, we knew that we wanted to avoid the burden of maintaining repositories full of home-brewed deployment scripts and domain-specific languages like YAML.